Maximizing Competitive Advantage: An Overview of Bowman's Strategy Clock (plus PPT)
Enhance Your Strategic Planning with Bowman's Strategy Clock: Access Our Detailed Overview and Download Free Templates for PowerPoint, PDF, and Google Slides
The Bowman Strategy Clock is a tool developed by Cliff Bowman to help organizations understand and analyze their competitive position in the market.
It is based on the idea that organizations can use eight strategies to differentiate themselves from their competitors and achieve a competitive advantage.
Our Bowman's Strategy Clock template helps you navigate the competitive landscape to improve your business strategy.
Bowman’s Strategy Clock in a Nutshell
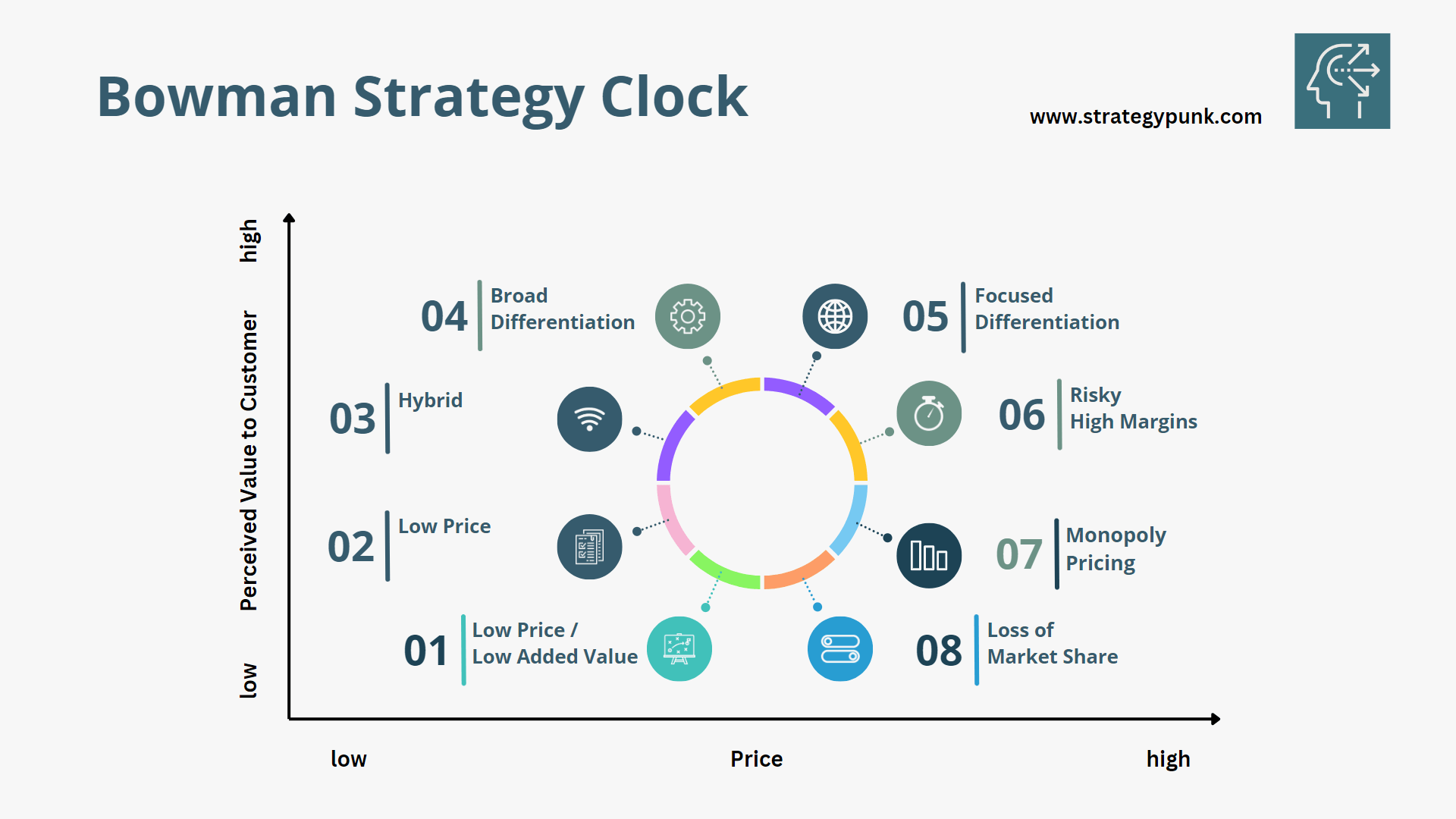
Bowman's Strategy Clock is a model that helps companies analyze their competitive position and potential strategies for improvement. It is represented by a clock face divided into eight segments, each representing a different competitive position.
The segments are low-cost provider, broad differentiation, focused low cost, focused differentiation, integrated low cost/differentiation, market niche/niche differentiation, market niche/niche low cost, and market niche/niche integrated low cost/differentiation.
Each segment corresponds to a different competitive strategy for achieving a competitive advantage. The model helps companies identify their current position and potential strategies for improvement.
What are the 8 positions of Bowman's strategy clock?
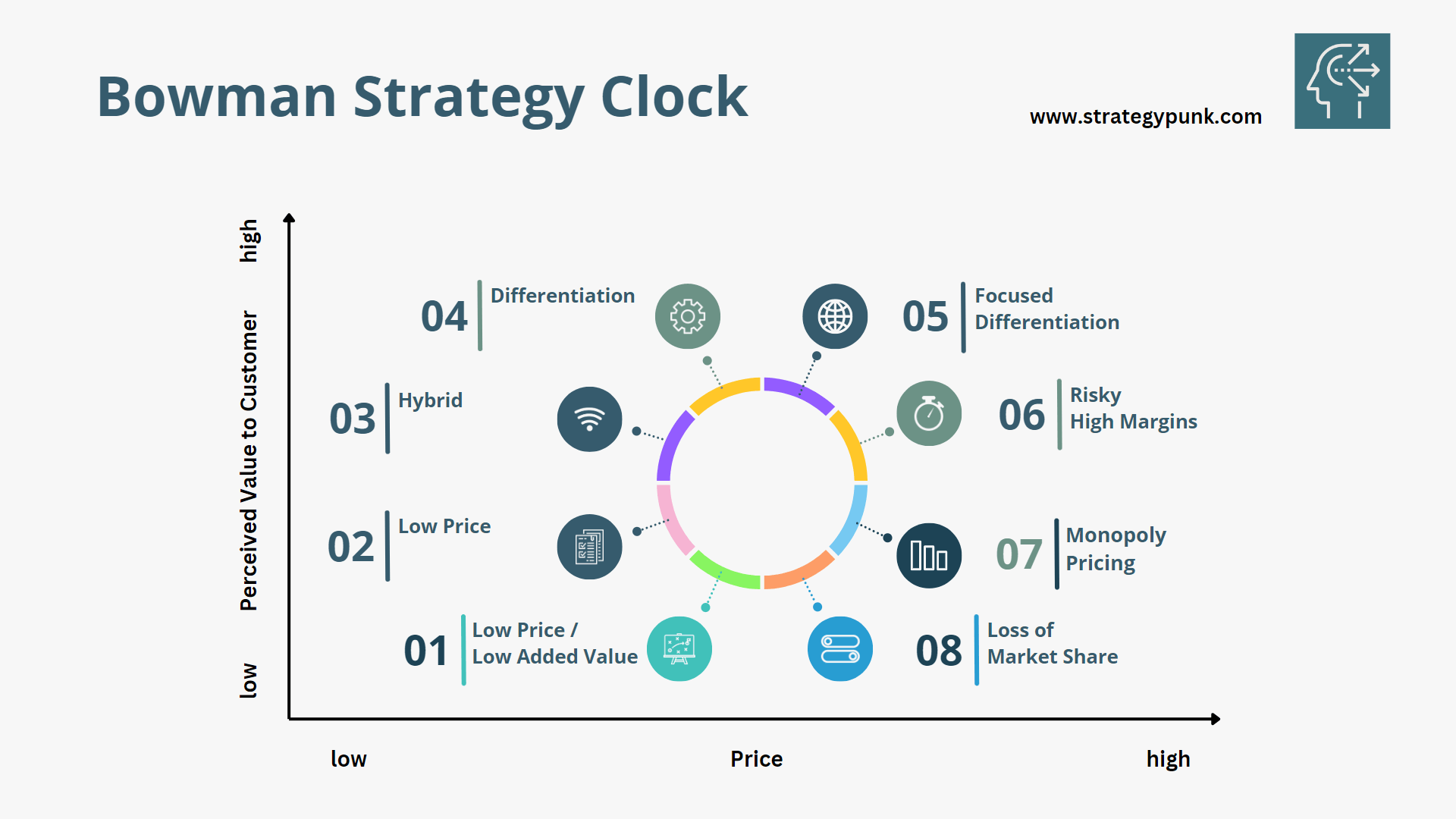
The eight strategies represented on the Bowman Strategy Clock are:
1. Low Price / Low Added Value
In Bowman's Strategy Clock model, the "low-cost provider" segment represents a competitive strategy where a company focuses on providing its products or services at the lowest possible price while offering little added value.
Companies often use this strategy in highly price-sensitive markets with limited differentiation opportunities. Companies that adopt this strategy need a very efficient and low-cost operational structure, and they typically target price-sensitive customers looking for the lowest-priced products or services.
This strategy can be very effective in winning market share, but it can also lead to low-profit margins, and companies may need help increasing their prices in the future.
2. Low Price
This segment represents a competitive strategy where a company focuses on providing its products or services at the "lowest possible price."
Companies that follow this strategy often produce large quantities of products to exploit economies of scale. By making large quantities, they can reduce their unit costs and offer their products or services at a lower price than their competitors. They also typically focus on cutting costs in all areas of the business, such as by using low-cost materials and production methods, reducing labor costs, and reducing overhead expenses.
This enables them to offer their products or services at a lower price than competitors while maintaining profitability.
3. Hybrid (Moderate Price/Moderate Differentiation)
In Bowman's Strategy Clock model, the "moderate price/ moderate differentiation" segment represents a competitive strategy where a company balances the goals of providing products or services at a moderate price while offering moderate differentiation.
Companies operating in markets often use this strategy with a balance of price-sensitive and value-conscious customers. Companies adopting this strategy typically focus on balancing cost and differentiation by offering a mix of low-cost and differentiated products or services. They may also use this strategy in different areas of their business.
This strategy can be challenging to implement but can lead to a competitive advantage by appealing to a broad range of customers.
4. Broad Differentiation
The "Broad differentiation" segment represents a competitive strategy where a company differentiates itself from its competitors by offering a wide range of products or services that are unique and superior in some way.
This strategy is often used by companies that operate in markets where customers have diverse needs and preferences. Companies that adopt this strategy typically invest heavily in product development, marketing, and branding to create a strong and unique value proposition.
This strategy can be very effective in creating a strong brand and loyal customers, but it can also be costly and difficult to maintain.
5. Focused Differentiation
The "Focused differentiation" segment represents a competitive strategy where a company differentiates itself from its competitors by focusing on a specific niche market and offering products or services that are unique and superior in that niche.
This strategy is often used by companies operating in markets with a limited number of customers with specific needs or preferences. Companies adopting this strategy invest heavily in product development, marketing, and branding to create a strong and unique value proposition that appeals to their target market.
This strategy can be very effective in creating a strong brand and loyal customers within the niche, but it can also be costly and difficult to maintain.
These strategies involve charging a premium price for a unique and superior offering. However, these strategies come with risks like competition imitation, market saturation, and the need for constant innovation and adaptation.
6. Risky High Margins
The "Risky High Margins" segment charges a premium price for a unique and superior offering.
However, these strategies come with risks like competition imitation, market saturation, and the need for constant innovation and adaptation.
7. Monopoly Pricing
The "Monopoly pricing" segment refers to a situation where a company has exclusive control over the supply of a product or service and can, therefore, charge higher prices than would be possible in a competitive market. In this case, the company may not have any direct competitors and can use its market power to set higher prices than the cost of production.
This can lead to higher profit margins for the company and adverse consumer effects, such as reduced access to the product or service and increased prices.
It's important to note that Monopoly pricing is illegal in most countries, and antitrust laws regulate it.
8. Loss of Market Share
The "Loss of market share" segment refers to a decrease in a company's percentage of total sales or customers in a given market. This strategy involves products with low perceived value but disproportionately high pricing.
This can happen for various reasons, such as increased competition, changing market conditions, or failing to adapt to new trends or technologies.
To prevent losing market share, companies should continually monitor their market and competitors, identify opportunities for improvement, and adapt their strategies accordingly.
What is Bowman's clock strategy used for?
Using the Bowman Strategy Clock, organizations can analyze their current strategy and determine whether it is effective or whether they should consider shifting to a different approach to achieve a competitive advantage.
Each segment corresponds to a different competitive strategy for achieving a competitive advantage. The model helps companies identify their current position and potential strategies for improvement.
What are the two essential elements of Bowman's strategy clock?
The Bowman Strategy Clock is a tool that helps organizations understand and analyze their competitive position in the market. It is based on the idea that organizations can use eight strategies to differentiate themselves from their competitors and achieve a competitive advantage.
There are two critical elements of the Bowman Strategy Clock:
- Differentiation: The degree to which an organization's products or services are perceived as unique and different from its competitors.
- Cost: The price an organization charges for its products or services relative to its competitors.
Combining these elements determines the organization's strategic position on the Bowman Strategy Clock. For example, an organization offering unique, high-quality products at a lower price than its competitors may be in a strong strategic position. In contrast, an organization that cannot differentiate itself from its competitors and has high prices may be at a competitive disadvantage.
By analyzing their position on the Bowman Strategy Clock, organizations can identify their current competitive strategy and consider whether it is effective or should be replaced to achieve a competitive advantage.
What is the most desirable strategic position on Bowman's clock?
The most desirable strategic position on the Bowman Strategy Clock will depend on the individual or organization's specific goals and circumstances. There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question.
That being said, some strategies may be more generally desirable in certain circumstances. For example, the cost leadership strategy (position one on the clock) may be particularly appealing for organizations operating in highly competitive markets with low margins, allowing them to differentiate themselves by offering lower prices. The differentiation strategy (position two on the clock) may appeal more to organizations with unique products or services that customers value, as it allows them to command higher prices and capture a larger market share.
Ultimately, the most effective strategy will depend on the specific goals of the organization and the resources and capabilities it has at its disposal. It is essential for organizations to carefully consider their competitive position and the needs of their target market to identify the strategy that is most likely to lead to success.
Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
free and fully editable PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
The Bowman's Strategy Clock PowerPoint template is a visual tool that can be used to present the eight segments of Bowman's Strategy Clock model.
This template can help explain the different competitive positions and strategies a company can adopt and help your audience understand how to use the model to analyze their competitive situation.
In short, the template will help you present Bowman's strategy clock clearly and concisely, making it easy for your audience to understand and follow the concept.