PESTLE Analysis of TSMC (FREE PDF Template)
Download a free PDF PESTLE analysis of TSMC's latest annual report, including a company introduction and strategy description.

Short Introduction to TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is a dedicated semiconductor foundry established in 1987 and headquartered in the Hsinchu Science Park, Taiwan.
- It pioneered the pure-play foundry business model, which means it exclusively manufactures its customers’ products and does not design, manufacture, or market any semiconductor products under its name.
- TSMC enables the success of fabless companies and Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) by providing advanced and specialty technologies, mask technologies, 3DFabric® advanced packaging, silicon stacking technologies, and design ecosystem support.
- As of 2023, TSMC manufactured 11,895 products using 288 distinct technologies for 528 other customers.
- TSMC’s global customer base produces semiconductors for various applications and end markets, including high-performance computing, smartphones, the Internet of Things (IoT), automotive, and digital consumer electronics.
- This diversification allows TSMC to maintain high capacity utilization and profitability.
- The company is publicly traded on the Taiwan Stock Exchange (TWSE) and the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
- It operates multiple GIGAFAB® facilities, primarily in Taiwan, with expansion into overseas locations like Arizona and Japan.
- TSMC is committed to sustainability and corporate social responsibility, adhering to international standards and best practices in environmental, safety, and health management.
TSMC's Strategy
TSMC's strategy centers around three competitive strengths: Technology Leadership, Manufacturing Excellence, and Customer Trust.
These strengths are supported by a pure-play foundry business model that prioritizes enabling customer success by exclusively manufacturing products for its clients without competing in the market with its prioritized products.
Critical elements of TSMC's strategy are as follows:
Technology Leadership
- Leading-edge technologies: TSMC aims to be the first dedicated foundry to offer leading-edge, next-generation technologies, such as the 2-nanometer and 14-Angstrom nodes. This requires substantial and continuous research and development (R&D) investment, amounting to 8.5% of revenue in 2023.
- Comprehensive technology portfolio: TSMC offers various technologies, including advanced and specialty technologies and 3DFabric® advanced packaging and silicon stacking solutions. This provides customers with options to meet diverse application needs.
- Open Innovation Platform (OIP): TSMC's OIP initiative promotes collaboration with ecosystem partners, including EDA vendors, IP providers, and design service companies. This collaborative approach accelerates innovation, reduces design time, and enhances the value TSMC delivers to customers.
Manufacturing Excellence
- GIGAFAB® facilities: TSMC operates large-scale, highly efficient GIGAFAB® facilities to ensure reliable production capacity and consistent quality. The company employs a centralized management system to coordinate these facilities and achieve operational excellence.
- Agile and intelligent operations: TSMC integrates advanced technologies, such as AI and machine learning, into its manufacturing processes to improve efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness. This includes initiatives like Intelligent Fab, which uses AI to optimize production, equipment maintenance, and quality control.
- Global manufacturing footprint: TSMC strategically expands its manufacturing presence beyond Taiwan to locations like Arizona, Japan, and Europe. This global expansion aims to enhance customer proximity, diversify supply chain risks, and address geopolitical concerns.
Customer Trust
- Customer-centric approach: TSMC prioritizes customer success and builds enduring relationships through close collaboration and exceptional service. This includes providing dedicated customer support teams, regular communication, and responsiveness to customer feedback.
- Robust quality and reliability: TSMC implements rigorous quality control measures and strives to meet or exceed customer expectations for product performance and reliability. This commitment to quality contributes to TSMC's reputation as a trusted foundry partner.
- Strong diversification: TSMC serves a diverse customer base across various end markets, such as high-performance computing, smartphones, IoT, automotive, and digital consumer electronics. This diversification helps mitigate risks associated with demand fluctuations in specific sectors.
By focusing on these strategic pillars, TSMC aims to maintain its position as the world's leading semiconductor foundry, capture a significant share of industry growth, and deliver value to its customers and shareholders.
PESTLE Analysis of TSMC
Here is a PESTLE analysis of TSMC based on the 2023 annual report and letter to shareholders.
Political
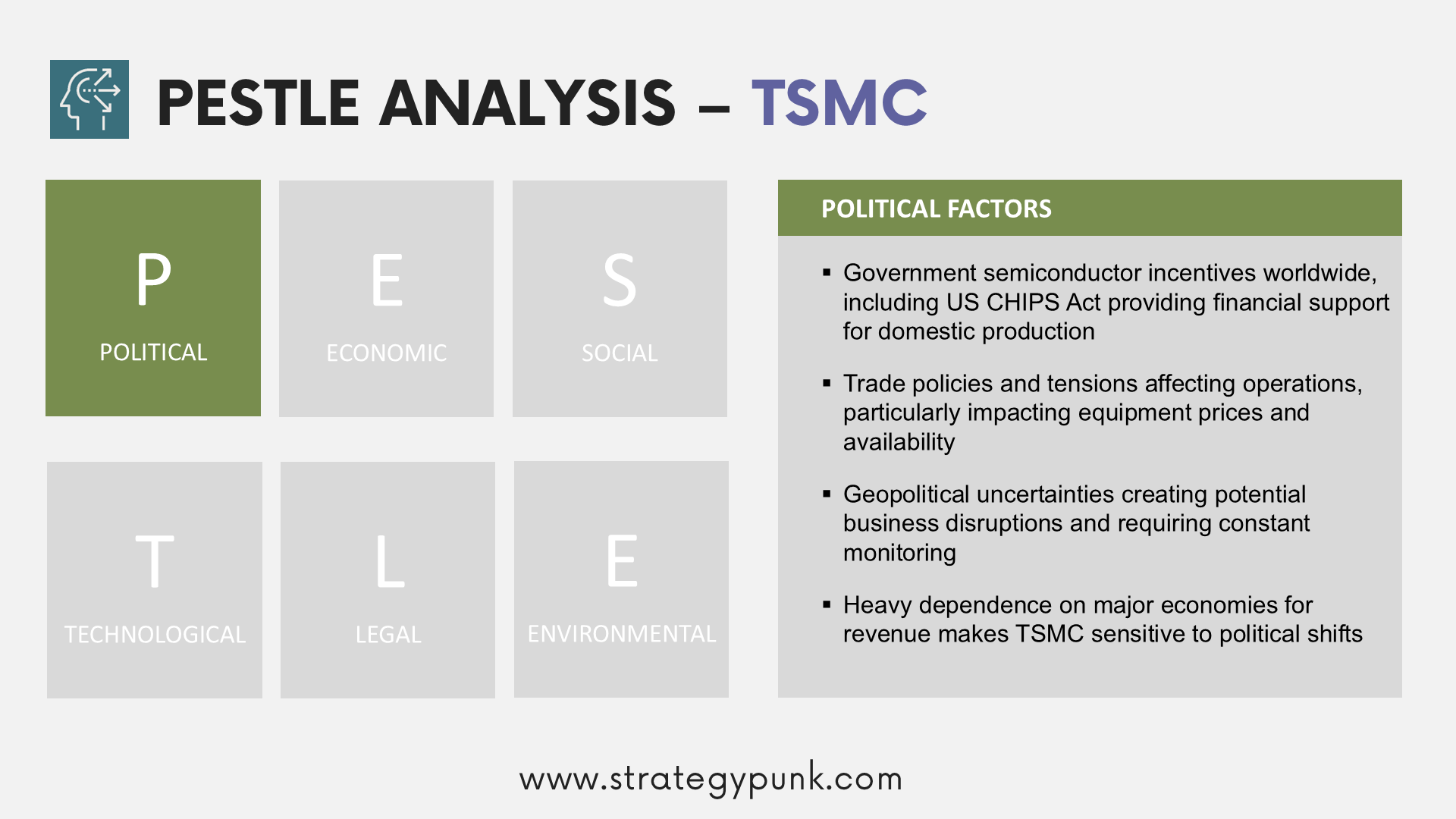
- Government incentives and support for the semiconductor industry: Governments worldwide provide incentives to promote their domestic semiconductor industries. For example, the US CHIPS Act offers financial incentives to bolster the US semiconductor sector. While TSMC has received and may receive financial incentives in the future, there's no guarantee of their availability or the level of support. Governments may impose conditions on these incentives, potentially impacting TSMC's operations.
- Trade policies and tensions: Changes in trade policies, such as increased tariffs, import and export controls, and trade barriers, can affect TSMC and its customers, impacting operating results. TSMC generates most of its revenue from sales to significant economies, making it vulnerable to trade policy shifts in those regions. The sources highlight ongoing trade tensions and their potential to disrupt equipment prices and availability, with consequences for TSMC's financial performance. TSMC acknowledges the need to monitor and adapt to evolving trade policies.
- Geopolitical uncertainties: Geopolitical tensions are cited as potential factors impacting TSMC’s business. The sources don't elaborate on specific geopolitical risks, but their acknowledgment suggests that TSMC is exposed to political events and international relations.
Economic
- Global macroeconomic conditions: The sources mention weakening global macroeconomic conditions and higher inflation and interest rates as challenges for the semiconductor industry. These factors can influence consumer sentiment and demand for electronic devices, affecting TSMC's revenue. The sources highlight economic risks like interest rate fluctuations and foreign exchange volatility. TSMC primarily earns revenue in US dollars but incurs capital expenditures in other currencies, exposing it to fluctuations in exchange rates, particularly the US dollar against the New Taiwan dollar.
- Semiconductor industry cyclicality: The semiconductor industry is inherently cyclical, experiencing periods of growth and decline. TSMC acknowledges that industry downturns and overcapacity can reduce demand for its foundry services. Fluctuations in demand can lead to volatility in TSMC's revenue and earnings.
Social
- Demand for energy-efficient computing: TSMC recognizes the increasing need for energy-efficient computing. The company's development of advanced technologies like the 2-nanometer node, focusing on density and energy efficiency, reflects this trend. TSMC aims to address sustainability concerns by investing in energy-saving and carbon-reduction initiatives. The company is also committed to responsible sourcing and waste management.
- Talent acquisition and development: The sources emphasize the importance of human capital for TSMC's success. TSMC faces challenges in recruiting and retaining skilled technical and professional personnel. The company invests in talent development programs and initiatives to attract and retain a qualified workforce. Competition for talent, especially in the semiconductor industry, risks TSMC's ability to meet its personnel needs.
- Shifting consumer preferences and market trends: Rapidly changing consumer preferences and technology adoption patterns affect TSMC's products and services demand. TSMC needs to constantly adapt its offerings to cater to evolving market trends, such as the rise of consumer-driven products like smartphones. The sources highlight the importance of agility and quick response to market changes.
Technological
- Rapid technological advancements: TSMC operates in a highly dynamic environment with constant technological innovation. A key challenge is keeping pace with Moore's Law and developing increasingly sophisticated semiconductor technologies. TSMC invests heavily in research and development (R&D) to maintain its technology leadership. The sources mention TSMC's efforts in developing advanced nodes like the 2-nanometer and 14-Angstrom technologies.
- AI and HPC as growth drivers: TSMC identifies artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) as significant growth opportunities. The company provides advanced technologies and design solutions to support AI and HPC applications. TSMC's development of HPC-focused technologies like N4X and N3X exemplifies its focus on these areas.
- Cybersecurity threats: TSMC acknowledges the increasing threat of cyberattacks, which could disrupt its operations or compromise sensitive information. Despite investing in cybersecurity measures, the company recognizes the evolving nature of cyber threats and the need for continuous vigilance.
Legal
- Intellectual property (IP) protection: TSMC highlights the importance of protecting its IP, customers, and partners. The sources mention the risk of IP infringement, particularly during overseas expansion. TSMC has policies and procedures to safeguard its IP and emphasizes a culture of respect for intellectual property rights.
- Environmental regulations and sustainability requirements: TSMC operates in a sector with stringent environmental regulations. The sources highlight TSMC's commitment to environmental protection, including initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve energy, and manage waste. TSMC has obtained certifications like ISO 14001 and ISO 50001, demonstrating its adherence to environmental management standards.
- Compliance with labor laws and regulations: TSMC operates globally and must comply with labor laws in different jurisdictions. The sources mention TSMC's policies and practices regarding employee safety, health, and working conditions. The company conducts workplace hazard assessments, provides safety training, and has procedures for managing hazardous materials.
Environmental
- Climate change and resource scarcity: TSMC acknowledges climate change as a significant risk and has adopted the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations to assess its impact. The sources outline TSMC's efforts to reduce its environmental footprint, including energy conservation, renewable energy use, and water management. TSMC aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 and has set short-term and long-term targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Natural and artificial disasters: TSMC's operations are vulnerable to natural disasters such as earthquakes, typhoons, and droughts. The sources also mention artificial disasters like fires, cyberattacks, and supply chain disruptions. TSMC has business continuity management plans and practices to mitigate the impact of such events.
TSMC PESTLE PDF Template
Unlock valuable insights into TSMC's business environment with our detailed PESTLE analysis.
This report delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors influencing one of the world's leading technology companies.
It is ideal for students, professionals, and enthusiasts looking to understand the external forces shaping TSMC's strategies and market position.
Please stay tuned to learn about the challenges and opportunities for TSMC.