Retrenchment Strategy Simplified and Explained (Free PDF template)
Unlock the secrets of Retrenchment Strategy with our comprehensive guide. Simplified & Explained, this Free PDF template offers key insights & strategies for effective downsizing. Download now to navigate challenges with confidence.

Introduction
Retrenchment strategy refers to a company's steps to reduce costs, streamline operations, and focus on core business activities to improve financial performance. This strategy is often used when a company faces financial difficulties, intense competition, or needs to realign its priorities. The goal is to cut expenses, eliminate inefficiencies, and double down on the most profitable business units.
When executed correctly, a retrenchment strategy can help stabilize a struggling company and set it toward recovery. However, reduction also involves difficult decisions regarding layoffs, asset sales, and market exits, which can negatively impact employees and reputation. Companies must weigh these risks carefully when considering a retrenchment approach.
Download the free Retrenchment Strategy PDF template below.
What is a Retrenchment Strategy?
A retrenchment strategy aims to improve a company's financial situation by reducing operating costs and eliminating inefficient or unprofitable business areas.
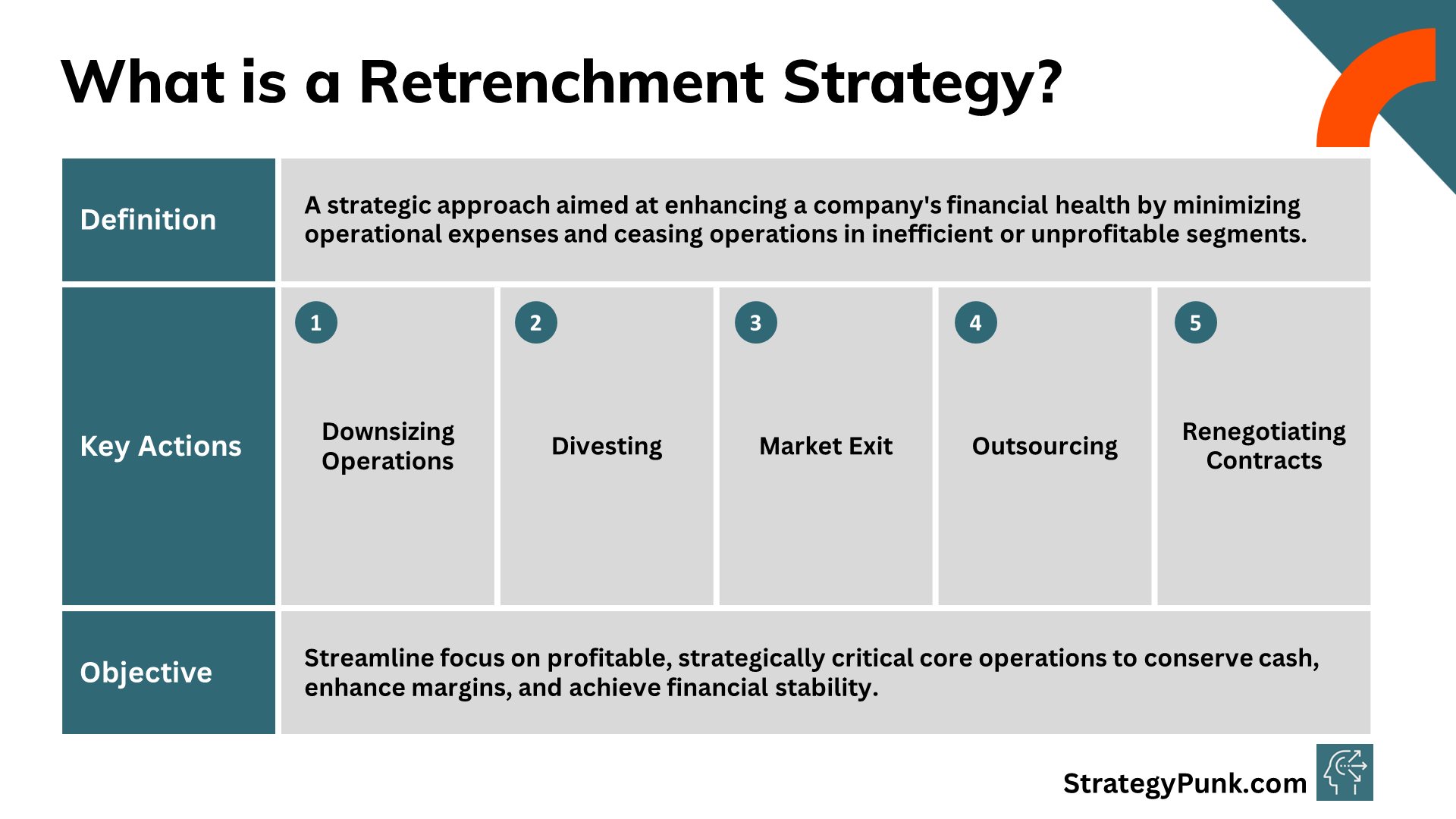
This typically involves actions such as:
- Downsizing operations by cutting jobs, closing facilities, or reducing inventory/assets
- Eliminating or divesting unprofitable product lines, business units, or assets
- Exiting specific geographic markets that are no longer financially viable
- Outsourcing non-essential functions to external vendors
- Renegotiating contracts with suppliers to reduce purchase costs
The goal is to focus resources on the company's most profitable and strategically essential core operations. This allows a struggling company to conserve cash, boost margins, and return to stability.
Types of Retrenchment Strategy
Corporate retrenchment strategies are approaches organizations take to reduce scale or scope to address challenges, improve financial stability, or realign resources with current objectives.
These strategies are often implemented in response to declining performance, economic downturns, or shifts in the market environment.
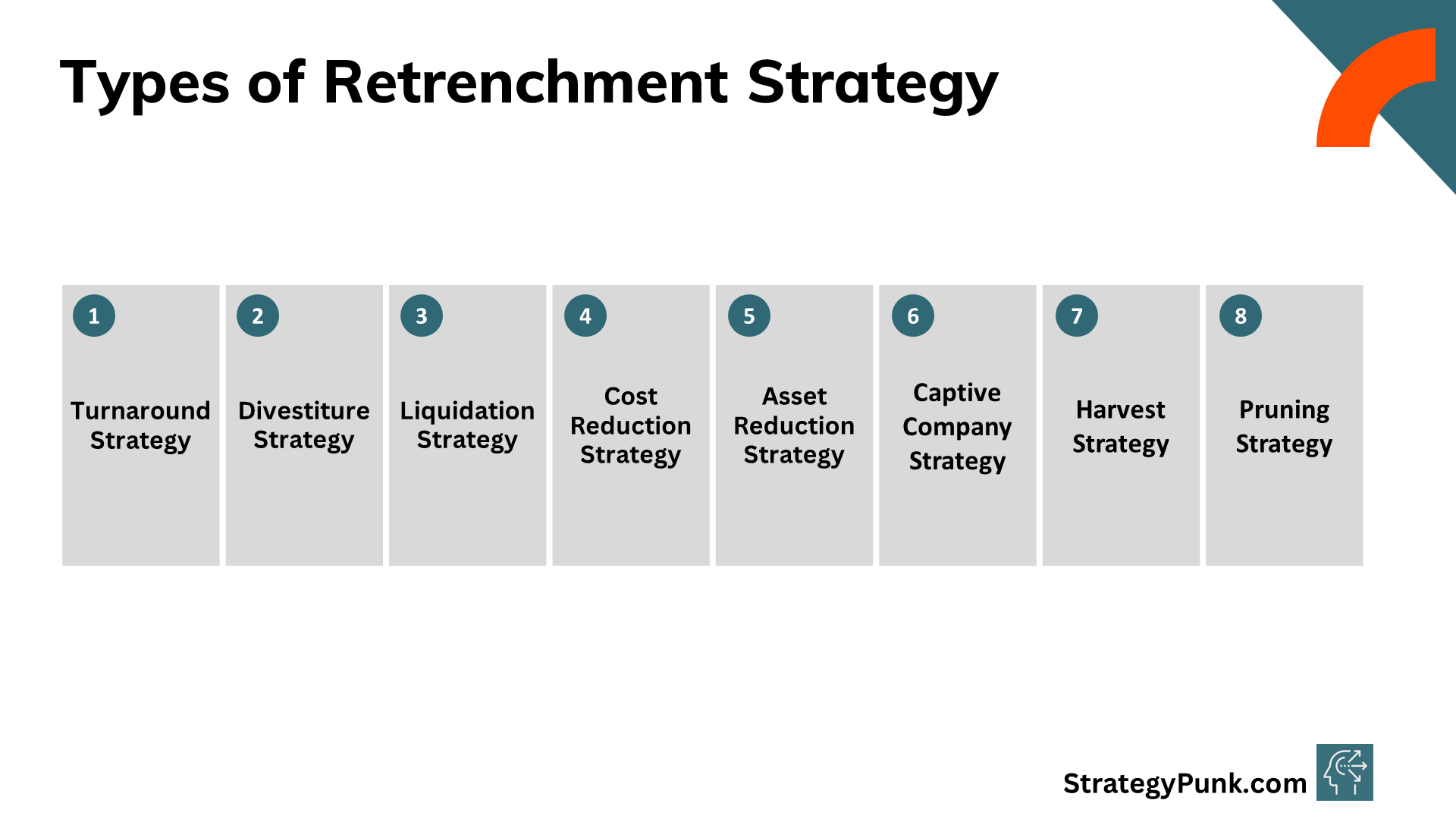
The common types of retrenchment strategies include:
Turnaround Strategy
This involves actions to reverse a company's decline and restore profitability. It may include cost-cutting measures, business reorganization, improvement in productivity, and sometimes refocusing on core activities.
Divestiture Strategy
This entails selling off a portion of a company, such as a division or subsidiary, underperforming or not aligned with the core business. The goal is to raise capital, reduce debt, and focus more closely on areas with the most potential for growth or profitability.
Liquidation Strategy
This is the most extreme form of reduction, involving the closure and sale of the entire company's assets. This strategy is usually a last resort when the company cannot survive due to insurmountable challenges.
Cost Reduction Strategy
This strategy focuses on reducing operational expenses to improve financial performance. Measures can include reducing the workforce and marketing expenses, renegotiating contracts, and streamlining operations.
Asset Reduction Strategy
This is similar to cost reduction but more focused on tangible and intangible assets. Reducing the asset base and improving cash flow could involve selling underutilized assets, leasing instead of buying new equipment, or outsourcing parts of the business process.
Captive Company Strategy
In this approach, a company gives up independent operations in certain areas to become a supplier or distributor for a larger, more dominant company. This strategy can secure a steady business flow at the cost of losing some autonomy.
Harvest Strategy
Here, the company reduces investment in a product line or business segment to maximize short-term cash flow instead of long-term growth. This is often used in mature markets where further investment would lead to minor growth.
Pruning Strategy
This involves discontinuing products, services, or markets that do not meet expectations or align with the company's strategic goals. This is similar to a gardener pruning non-viable branches to encourage healthy growth.
Each strategy has its own implications and outcomes, and the choice among them depends on the organization's specific challenges and objectives.
What is Retrenchment Strategy Types Advantages and Disadvantages

Retrenchment strategies to reduce the scale or scope of a corporation's operations are critical during financial strain or strategic realignment.
Here, we delve into the advantages and disadvantages of different retrenchment strategy types, providing a more comprehensive understanding of their implications.
1. Turnaround Strategy
- Advantages:
- Can revitalize a failing company, restoring profitability and market position.
- Encourages a focus on core competencies and operational efficiency.
- May prevent the need for more drastic measures, like liquidation.
- Disadvantages:
- High risk of failure if not implemented correctly or if external conditions worsen.
- Requires significant managerial commitment and can lead to short-term financial strain.
- Often involves difficult decisions like layoffs, which can affect employee morale.
2. Divestiture Strategy
- Advantages:
- Generates cash by selling off non-core or underperforming assets.
- Allows a company to focus on its core business areas, potentially improving overall performance.
- Reduces debt and financial strain by offloading parts of the business that are not contributing positively.
- Disadvantages:
- This can lead to a loss of synergies between the businesses and the core company.
- May negatively impact the company's market position or brand image.
- Finding buyers for underperforming assets can be challenging, potentially leading to losses.
3. Liquidation Strategy
- Advantages:
- Provides a way out for stakeholders in cases where the company is no longer viable.
- Ensures that creditors and investors can recover a portion of their investments.
- Stops ongoing losses, allowing stakeholders to focus on new opportunities.
- Disadvantages:
- Results in the complete shutdown of the company, with significant job losses.
- Stakeholders typically recover less than their total investment.
- Can damage the reputation of the company's leadership and brand.
4. Cost Reduction Strategy
- Advantages:
- Improves profitability by decreasing operational expenses.
- Enhances competitive advantage by allowing for lower pricing or higher margins.
- Can be implemented relatively quickly to address financial issues.
- Disadvantages:
- If poorly managed, it can lead to a decrease in product quality or employee morale.
- May only provide short-term relief if the underlying issues are not addressed.
- Excessive cost-cutting can harm the company's long-term growth prospects.
5. Asset Reduction Strategy
- Advantages:
- Improves cash flow by liquidating underutilized assets.
- Decreases maintenance and holding costs associated with surplus assets.
- Can lead to a more focused and efficient operational model.
- Disadvantages:
- May result in short-term revenue loss from the sale of assets.
- Could limit the company's ability to scale operations in the future.
- Potentially overlooks the strategic value of certain assets.
6. Captive Company Strategy
- Advantages:
- Ensures a steady revenue stream by aligning with a dominant partner.
- Reduces marketing and distribution costs by leveraging the partner's network.
- Can provide stability in volatile markets.
- Disadvantages:
- Limits the company's autonomy and ability to make independent strategic decisions.
- Reliance on a single partner increases vulnerability to their business risks.
- May prevent the company from pursuing other potentially lucrative opportunities.
7. Harvest Strategy
- Advantages:
- Maximizes short-term profits from declining products or markets.
- Frees up resources that can be reallocated to more promising areas.
- Can extend the profitability of mature products without additional investment.
- Disadvantages:
- Short-term focus may neglect long-term growth opportunities.
- It can damage the brand reputation if customers perceive the company as withdrawing support.
- Risks alienating loyal customers of the harvested products.
8. Pruning Strategy
- Advantages:
- Helps focus resources on profitable or strategically important areas.
- Can improve organizational efficiency and reduce complexity.
- Encourages a proactive approach to discontinuing underperforming products.
- Disadvantages:
- This may result in immediate revenue loss if discontinued products or services contribute marginally to overall sales.
- Can lead to customer dissatisfaction or loss, especially if the discontinued products or services have a loyal customer base.
- Risks losing market share to competitors if they continue to offer similar products or services that were pruned.
What are the Reasons For Retrenchment Strategy
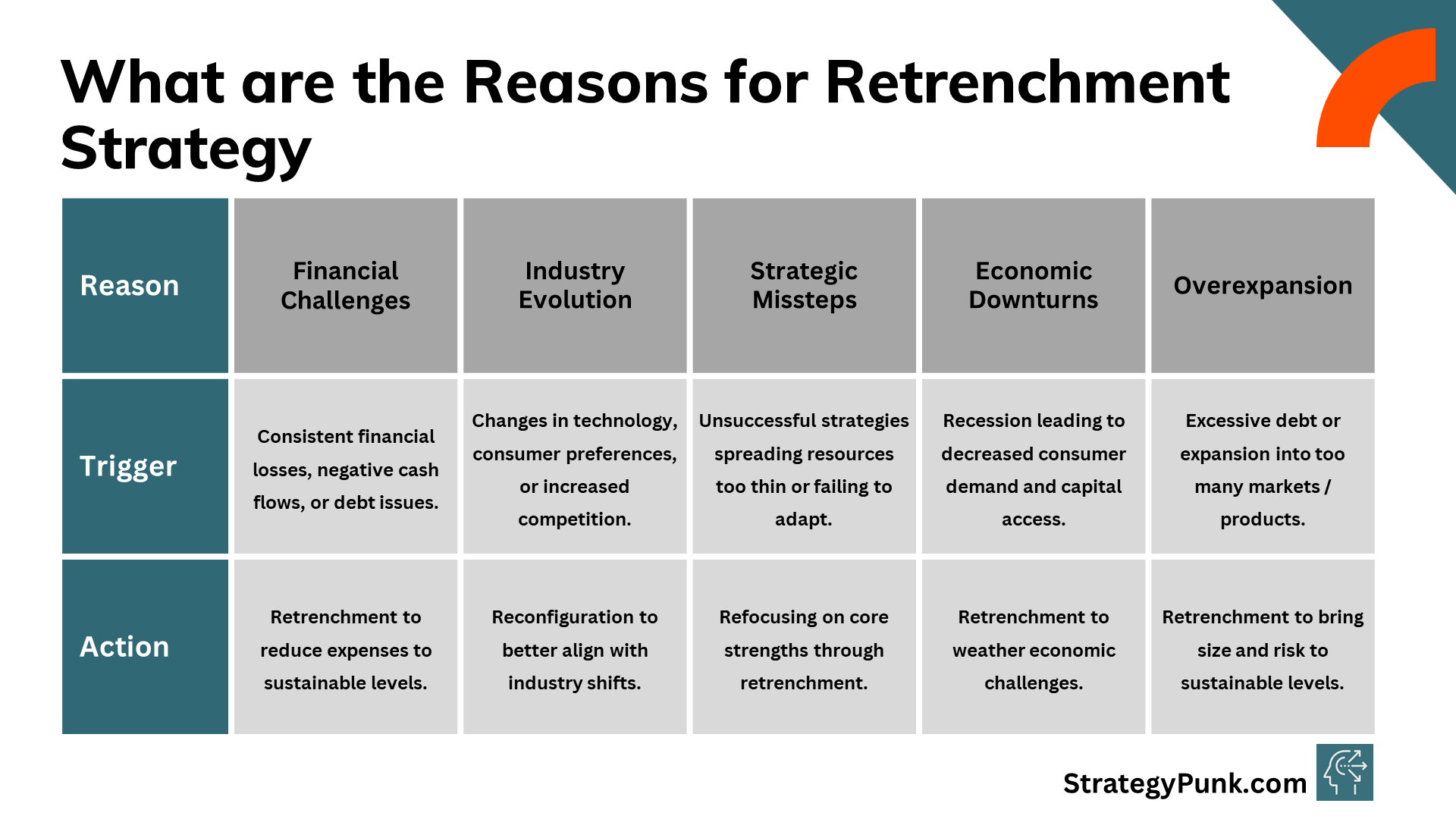
Several common triggers may prompt a company to pursue a retrenchment approach:
- Financial Losses - Consistent losses, negative cash flows, or debt troubles may force a company to make significant cuts to survive. Retrenchment reduces expenses to a level the company can afford.
- Industry Changes - Evolving technologies, consumer preferences, or increased competition may erode a company's market position. Retrenchment allows a company to reconfigure itself to better align with industry changes.
- Poor Strategic Decisions - Unsuccessful strategies that spread resources too thin or fail to adapt to market changes often necessitate a retrenchment process to correct course. This involves refocusing on core strengths.
- Economic Recession - External shocks like a recession can lead to lower consumer demand and reduced access to capital. Retrenchment becomes necessary for companies to weather the storm.
- Overexpansion - Some companies overexpand by taking on excessive debt or moving into too many markets/products. Retrenchment brings the size and risk profile back to sustainable levels.
When and why to implement retrenchment strategies
Retrenchment strategies are pursued when a company faces intense and prolonged financial distress or needs to fundamentally reshape itself and its priorities due to evolving market conditions and strategic missteps.
Common triggers that prompt retrenchment include:
- Steep industry decline that substantially erodes profits and market position
- The failure of a current business strategy that spreads resources too thin
- Lost competitive advantage from disruptive technology or competitors
- Economic recession that severely restricts access to capital
- Unsustainable debt obligations and cash flow issues
- Significant overexpansion into non-core business areas and tangential markets
- Changing consumer preferences or the emergence of a shrinking market that damages core products
The goals behind retrenchment are typically to:
- Avoid bankruptcy by drastically reducing expenses in line with revenue
- Mitigate further losses from non-performing business units and assets
- Withdraw from market segments and product lines where the competitive position has severely eroded
- Raise cash by shedding poorly integrated subsidiaries and unstable investments
- Refocus the business on core strengths and capabilities
Though often unavoidable, retrenchment is painful - involving layoffs, plant closures, and asset sales.
Leaders must pursue retrenchment strategies in a balanced manner that stabilizes finances while minimizing reputational and workforce damage.
Key steps in implementing retrenchment strategies
Executing an effective corporate retrenchment strategy involves several key steps:
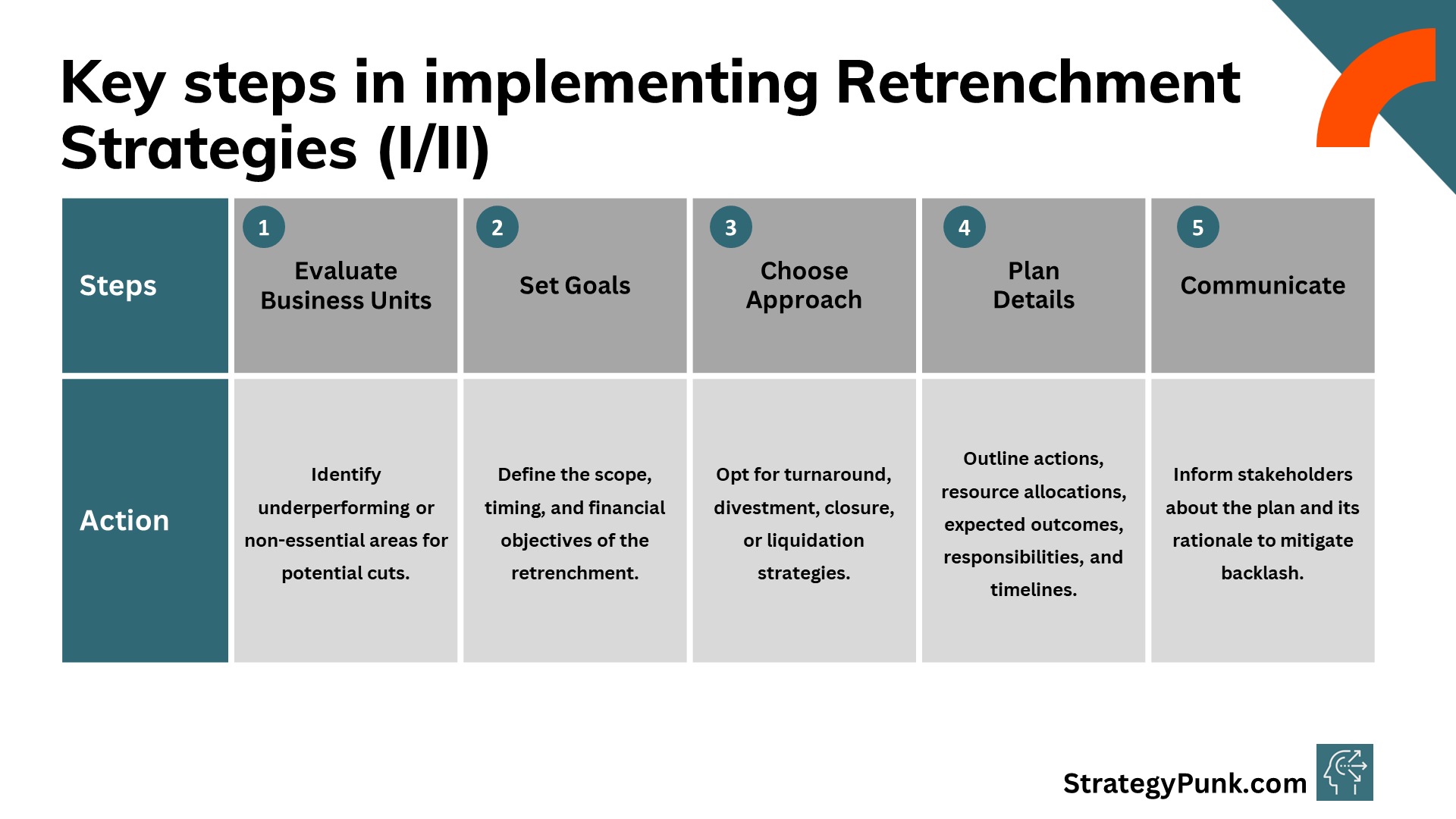
1. Evaluating business units and product lines – Identify poor performers and non-essential areas. Assess their tangible & intangible value.
2. Setting retrenchment goals – Define the scale, timing, and financial targets of the retrenchment strategy based on internal & external constraints.
3. Selecting a retrenchment approach - Choose suitable strategies for assessing struggling business units. The main options are turnaround, divestment, closure, or liquidation.
4. Developing a detailed retrenchment plan - Outline specific initiatives, resource allocations, expected results, and managers' accountability for execution and timelines.
5. Communicating changes - Be transparent with stakeholders about reasoning and implementation plans well in advance to ease uncertainty and backlash.
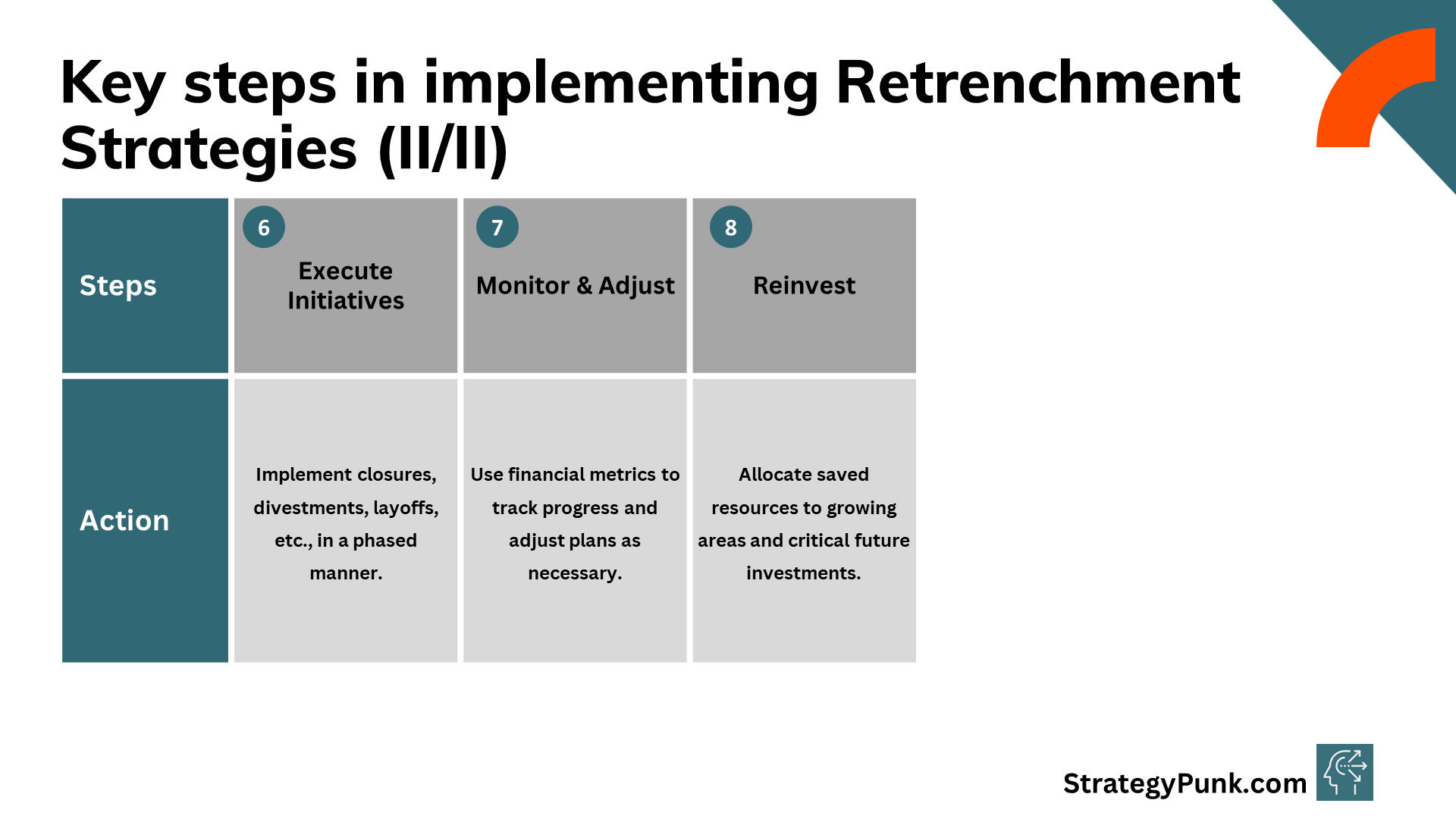
6. Executing initiatives - Carry out the closure of facilities, divestments of assets, job cuts, and other action plans in an organized, phased manner.
7. Tracking & Modifying—Monitor progress through financial metrics and benchmarks. Refine initiatives if targets aren't met. Manage morale.
8. Reinvestment - Shift resources freed from cuts into growing business units and investments critical for the future.
With proper planning and communication, companies can pursue necessary retrenchment while protecting workforce loyalty and corporate reputation.
Companies That Employed the Retrenchment Strategy
Many prominent companies have employed retrenchment strategies to navigate periods of industry upheaval or poor strategic decisions.
Some examples include:
IBM faced declining hardware sales in the 1990s. It retrenched by aggressively cutting costs, focusing on software and services businesses, and divesting printer and PC divisions.
Starbucks - Closed 800 underperforming stores in 2019 to concentrate resources on profitable locations and simplify operations.
Boeing—After the initial 737 MAX crashes in 2019, aircraft demand was reduced, Boeing cut production by 19%, and cost reductions were accelerated.
Kodak – Struggled to compete as digital photography displaced film. She pursued significant divestments, layoffs, and factory closures before eventually declaring bankruptcy.
General Motors - Took bailout funds in 2009. Filed bankruptcy and pursued plant closures, brand sales, layoffs, and other cuts before recovering profitability.
Groupon – Wildly overexpanded after IPO, then retrenched by exiting several international markets in 2015 and laying off 1,100 employees.
Retrenchment strategies were crucial for regaining financial stability amidst industry change and past strategic missteps. However, excessive cuts without broader revitalization of competitive strengths carry risks.
Conclusion
Retrenchment strategies require challenging workforce and asset reduction decisions, usually under financial duress.
However, strategic cost cuts and resource reallocation to core strengths can stabilize struggling firms. Leaders must pursue balanced retrenchment plans that retain key capabilities and manage workforce morale amidst necessary cuts.
With conscientious planning and execution, companies can retrench into a renewed competitive position.
Frequently Asked Questions
on Retrenchment Strategy
What early warning signs may indicate a retrenchment strategy is necessary?
Early indicators include several consecutive quarters of revenue or profit declines, consistently missing financial targets, losing market share to rivals, being unable to service debts, or observing core products losing relevance.
What should leaders prioritize communicating when implementing a retrenchment strategy?
The reasons for retrenchment moves include the scope of cuts, expected results, timelines, and plans to reinvest resources into growth areas eventually. Transparent communication can ease uncertainty and backlash.
Is divestment or closure better during retrenchment?
Divestment generates cash from asset sales but involves losing control. Closure damages morale yet cuts costs. The context determines whether divestment is preferable if assets remain valuable or have turnaround potential.
How can companies balance the downsides of retrenchment strategies?
Providing severance & career transition help, giving ample notice before layoffs, and transparently conveying business realities can help ease the pain. Investing in culture and engagement initiatives for remaining employees also helps buffer damage.
Should core capabilities be cut during retrenchment?
Avoid cutting resources and talent critical to core capabilities that determine competitive position—even if iis expensiveve. The goal is strategic slimming to refocus on strengths, not blind across-the-board cuts.
What is the difference between a turnaround strategy and a retrenchment strategy?
The key differences between a turnaround strategy and a retrenchment strategy are:
- Scope: A turnaround strategy involves significant changes to transform and revive a struggling business, while a retrenchment strategy focuses more narrowly on cost-cutting and downsizing operations.
- Goal: A turnaround aims to rescue and rehabilitate a failing business, while retrenchment aims to stabilize finances and improve efficiency.
- Changes: A turnaround often entails significant strategic, operational, and management changes. Retrenchment involves more targeted cuts, such as divestments, layoffs, expense reductions, etc.
- Timing: A turnaround is implemented when a business is nearing failure. Retrenchment can be done proactively to improve finances.
- Outcome: A successful turnaround can lead to recovery and growth, while retrenchment brings stability but not necessarily growth.
In summary, a turnaround strategy is transformational to revive a struggling business, while a retrenchment strategy focuses on stabilization through targeted cost-cutting and downsizing.
Retrenchment can sometimes be the first phase of a turnaround response before more strategic changes. However, reduction alone may lead to a complete turnaround with operational and management changes.
What kind of strategy is retrenchment?
Retrenchment strategy refers to a corporate management tactic employed by businesses looking to reduce their size or operations to become more financially stable and improve operational efficiency. This strategy is often considered when a company faces financial difficulties, declining market share, or external pressures that negatively impact its performance. The aim is to help the company conserve resources, refocus on its core business areas, and stabilize its financial position for long-term survival and growth.
Retrenchment Strategy PDF Template
download now!
Our Retrenchment Strategy PDF Template is meticulously designed to guide you through the complexities of downsizing with grace and precision.
This invaluable resource offers a step-by-step approach to evaluating, planning, and implementing retrenchment strategies that minimize impact while maximizing efficiency.
Whether you're a seasoned executive or a budding entrepreneur, this template empowers you to navigate the challenging waters of organizational change and ensure that your business remains resilient and robust in the face of adversity.
Download now and transform how you approach retrenchment, turning potential setbacks into strategic opportunities for growth and revitalization.