Mastering Strategic Focus: Market Attractiveness vs Ability to Win Matrix (Free PPT)
Master your growth strategy! Use the Market Attractiveness vs. Ability to Win Matrix. Free PPT template included—focus where it matters!
Introduction
Businesses have limited resources. This makes it important to decide where to focus.
Companies must make strategic decisions about where to invest time, money, and effort to maximize growth and stay ahead of the competition. The Growth Opportunities Matrix or Market Attractiveness vs Ability to Win Matrix is a powerful tool that helps businesses identify and prioritize opportunities, ensuring that resources are allocated where they can make the most significant impact.
This blog explains the Growth Opportunities Prioritization Tool. It shows how it works and how you can use it. Download the free PDF and PPT template at the end of the blog post.
What Is a Market Attractiveness vs Ability to Win Matrix?
The Growth Opportunities Matrix is a decision-making tool. It helps businesses decide where to focus their efforts. The matrix uses two factors:
- Attractiveness: This measures the potential of an opportunity.
- Ability to Win: This measures your company’s chance of success.
Each opportunity is placed on the matrix. The result is a clear view of your priorities.
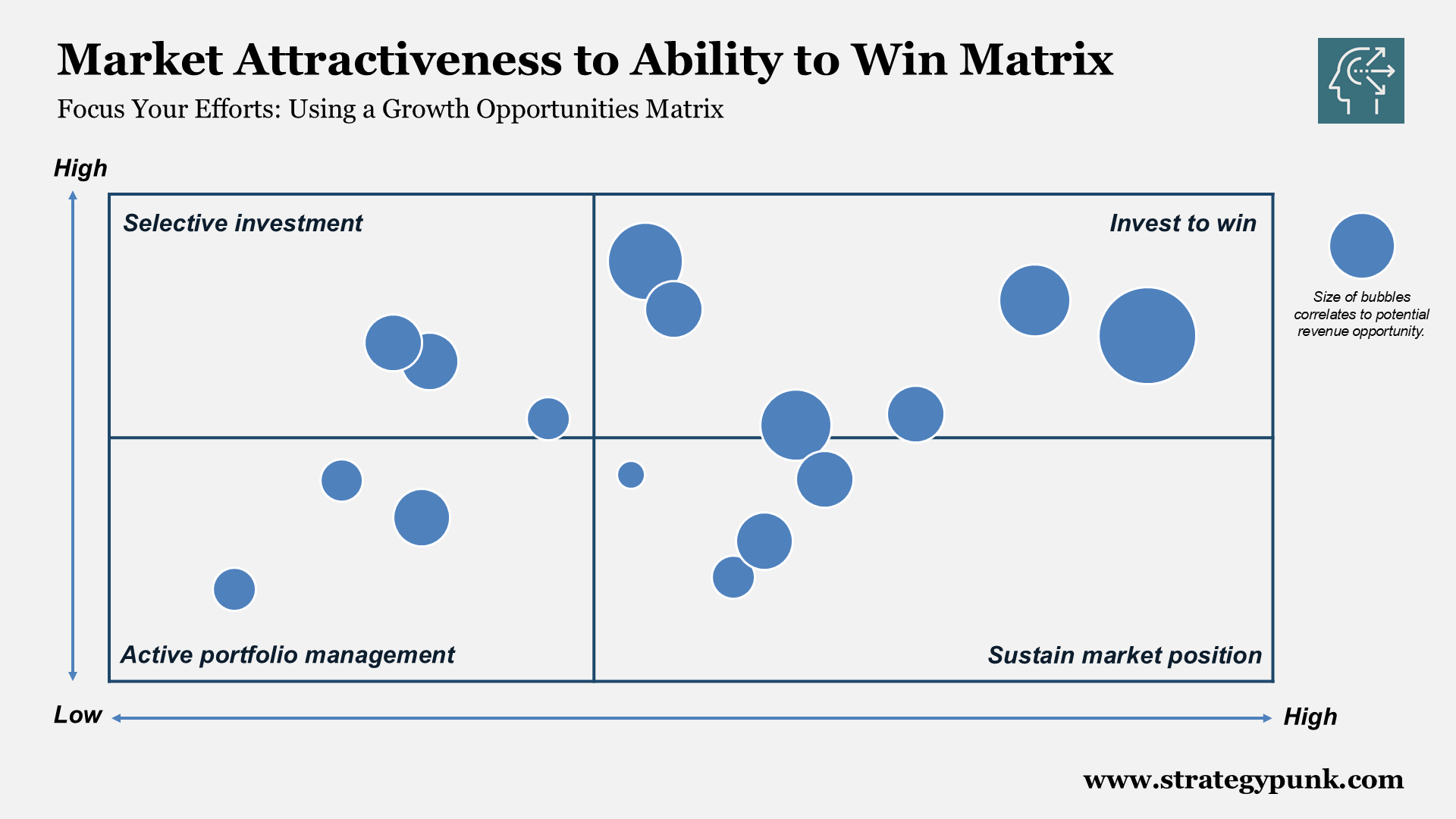
Market Attractiveness vs Ability to Win Matrix
Growth Opportunities Prioritization Tool, which helps identify where to focus resources based on two key dimensions:
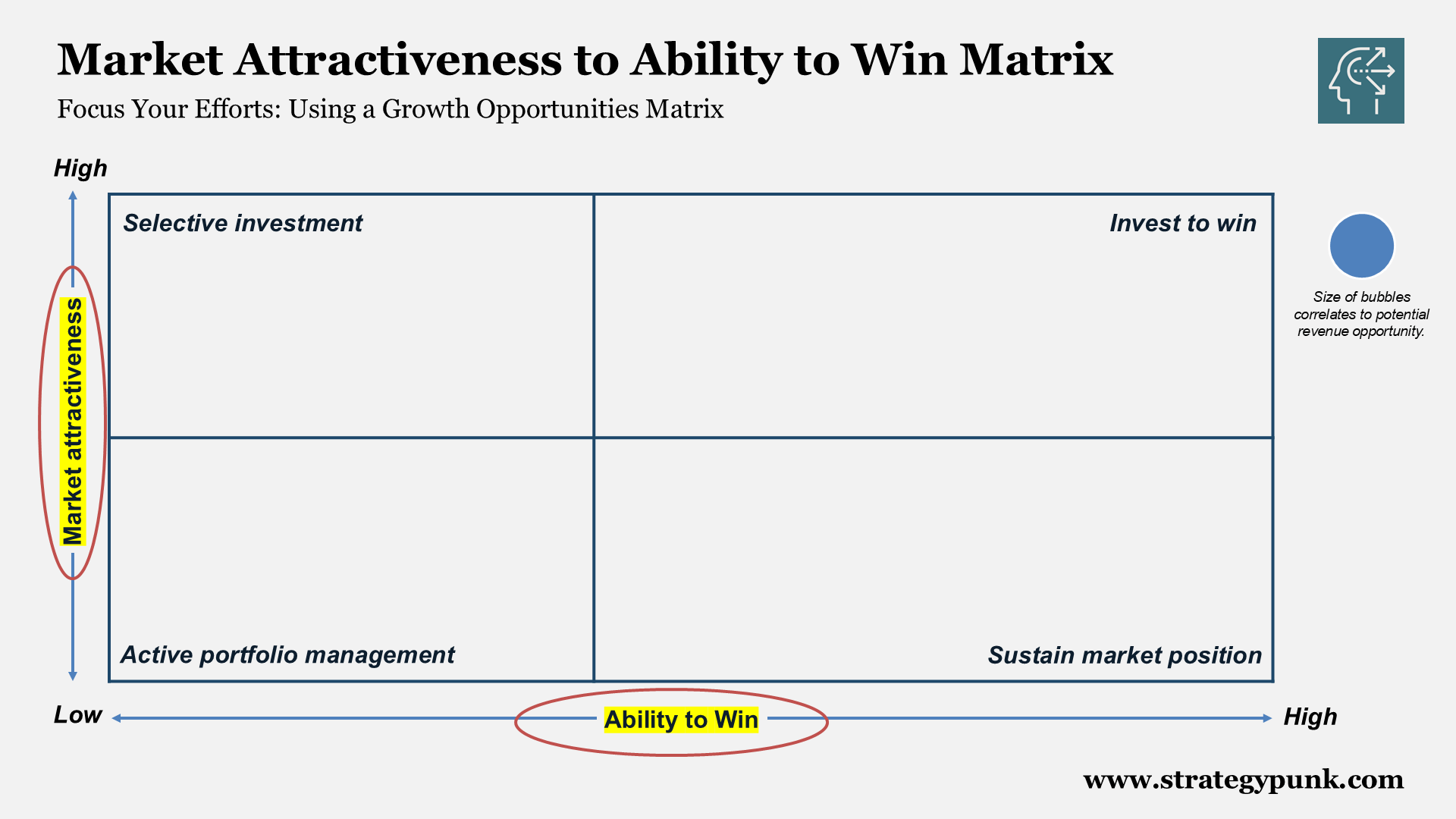
1. Market Attractiveness (Y-axis):
- Definition: Measures the market potential of an opportunity.
- Components: Includes factors such as:
- Market size: How large is the target market?
- Future growth: What is the projected growth rate of the market?
- Scale: High (more attractive) to Low (less attractive).
2. Ability to Win (X-axis):
- Definition: Assess your company’s competitive strength in seizing the opportunity.
- Components: Includes factors such as:
- Competitive position: How strong is the company compared to competitors?
- Customer feedback: How do customers perceive the company’s value proposition?
- Resources and effort: How much investment and effort is required to succeed?
- Scale: High (greater ability to win) to Low (less ability to win).
Quadrants Explained
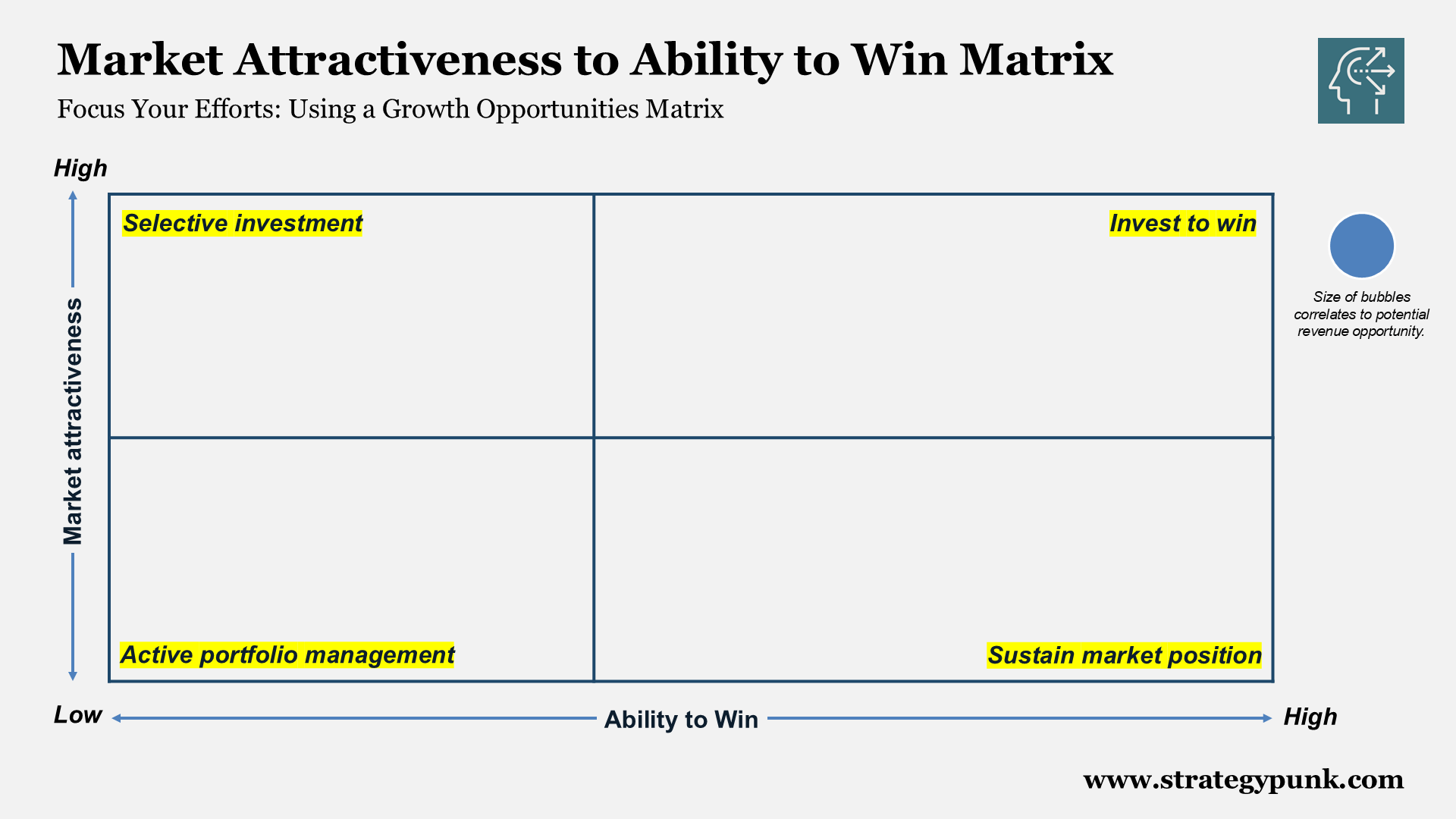
- Top-right (High Attractiveness, High Ability to Win - "Invest to Win"):
- Focus Area: These opportunities are highly attractive, and the company has a strong chance of winning.
- Strategy: Prioritize these for aggressive investment to maximize growth and returns.
- Top-left (High Attractiveness, Low Ability to Win - "Selective Investment"):
- Focus Area: Opportunities are attractive but your company’s ability to compete is weaker.
- Strategy: Invest selectively, possibly partnering or improving capabilities to compete effectively.
- Bottom-right (Low Attractiveness, High Ability to Win - "Sustain Market Position"):
- Focus Area: Opportunities where the company can win easily, but the market isn’t highly attractive.
- Strategy: Maintain your position but avoid over-investing.
- Bottom-left (Low Attractiveness, Low Ability to Win - "Active Portfolio Management"):
- Focus Area: These are low-priority opportunities regarding market attractiveness and ability to win.
- Strategy: Consider divesting or reallocating resources.
Bubble Size
Represents Potential Revenue Uplift: The larger the bubble, the greater the potential revenue opportunity if the full potential is realized.
Market Attractiveness to Ability to Win Matrix Example
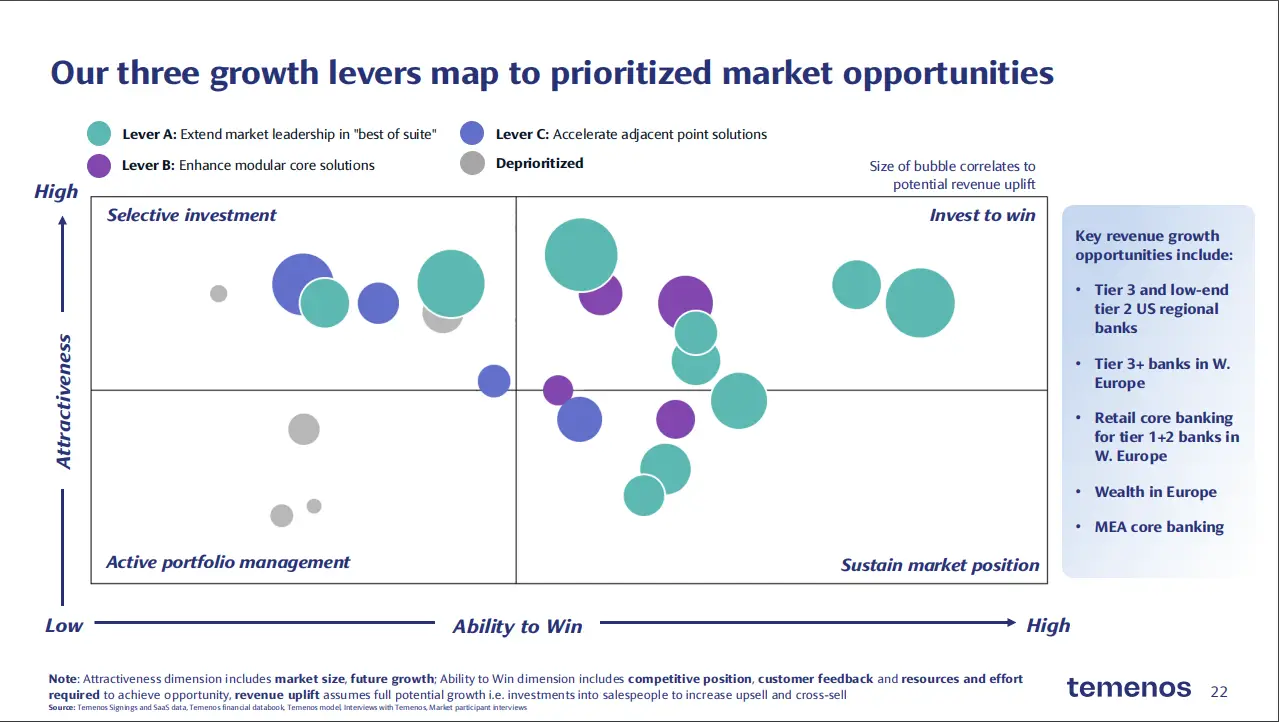
How to Use the Market Attractiveness vs Ability to Win Matrix
Step 1: Identify Opportunities
List all the opportunities you are considering. These could be new markets, products, or customer segments.
Step 2: Assess Attractiveness
For each opportunity, evaluate its market potential. Use data like market size and growth rates.
Step 3: Assess the Ability to Win
For each opportunity, evaluate your company’s position. Use data like customer feedback and competitive analysis.
Step 4: Place Opportunities on the Matrix
Use your ratings to place each opportunity on the matrix.
Step 5: Make Decisions
Focus on the top-right quadrant. Consider selective investment for the top-left. Maintain positions in the bottom-right. De-prioritize the bottom-left.
Why Use This Tool?
The Growth Opportunities Matrix is clear and visual. It simplifies complex decisions. It helps teams align on priorities.
This tool can help:
- CEOs set growth priorities.
- Marketing teams decide where to focus.
- Product managers choose which ideas to develop.
Applications
This matrix helps companies:
- Prioritize resource allocation.
- Make strategic decisions about which markets or products to invest in.
- Communicate a clear growth strategy to stakeholders.
Maximizing the Impact of the Market Attractiveness vs Ability to Win Matrix
To get the most out of the Growth Opportunities Matrix:
- Involve Cross-Functional Teams: Gather diverse perspectives from marketing, sales, operations, and finance.
- Use Objective Data: Base assessments on data rather than assumptions.
- Consider External Expertise: Consult industry experts or analysts when entering unfamiliar markets.
- Communicate Clearly: Ensure the rationale behind strategic decisions is understood across the organization.
Case study / Example
Imagine your company makes eco-friendly water bottles. You are looking at three opportunities:
- Expanding to a new country.
- Launching a luxury product line.
- Partnering with a fitness brand.
Step 1: Assess Attractiveness
- The new country has a large and growing market.
- The luxury market is smaller but growing fast.
- The fitness brand is well-known but niche.
Step 2: Assess the Ability to Win
- You have little presence in the new country.
- You have strong design capabilities for luxury.
- You have a good relationship with the fitness brand.
Step 3: Place on the Matrix
- The new country is in the top-left.
- The luxury line is in the top-right.
- The fitness brand is in the bottom right.
Step 4: Make a Decision
- Focus on the luxury line.
- Invest selectively in the new country.
- Maintain your fitness brand partnership.
New Perspectives and Insights
Integrating with Other Strategic Tools
The Growth Opportunities Matrix is most effective when used alongside other strategic frameworks:
- SWOT Analysis: Identify internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats.
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand the competitive dynamics of the industry.
- PESTEL Analysis: Consider macro-environmental factors (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal).
By combining insights from these tools, you can make more informed decisions.
Leveraging Data Analytics
In the digital age, data is a crucial asset:
- Big Data: Using large datasets to uncover market trends and customer behaviors.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecast future market developments.
- Customer Insights: Tailor offerings based on detailed customer profiles.
Embracing Agility
Markets are dynamic, and opportunities can shift rapidly:
- Regular Reviews: Reassess opportunities periodically to respond to changes.
- Flexible Strategies: Be prepared to pivot or adjust plans as needed.
- Innovation Culture: Encourage experimentation and learning.
Considering Global Trends
Stay informed about broader trends that can impact opportunities:
- Technological Disruptions: Emerging technologies can create new markets or render others obsolete.
- Economic Shifts: Global economic conditions can affect market attractiveness.
- Regulatory Changes: New laws or regulations can open up or restrict opportunities.
Download Your Market Attractiveness to Ability to Win Matrix Template
The Market Attractiveness vs. Ability to Win Matrix is a simple tool for deciding where to focus your business efforts. Use it to align your team and plan your growth.
Make smarter decisions with this matrix today.
Market Attractiveness vs Ability to Win Matrix PDF Template
To help you get started, we’re providing a free PowerPoint template below.
This customizable template allows you to plug in your vision, must-win battles, initiatives, enablers, and foundation to create a strategy that resonates with your organization.