Michael E. Porter Value Chain Analysis: Free PowerPoint Template
Free PPT & Google Slides template using Porter's Value Chain framework. Rate your company's capabilities. Fully editable. Download now.
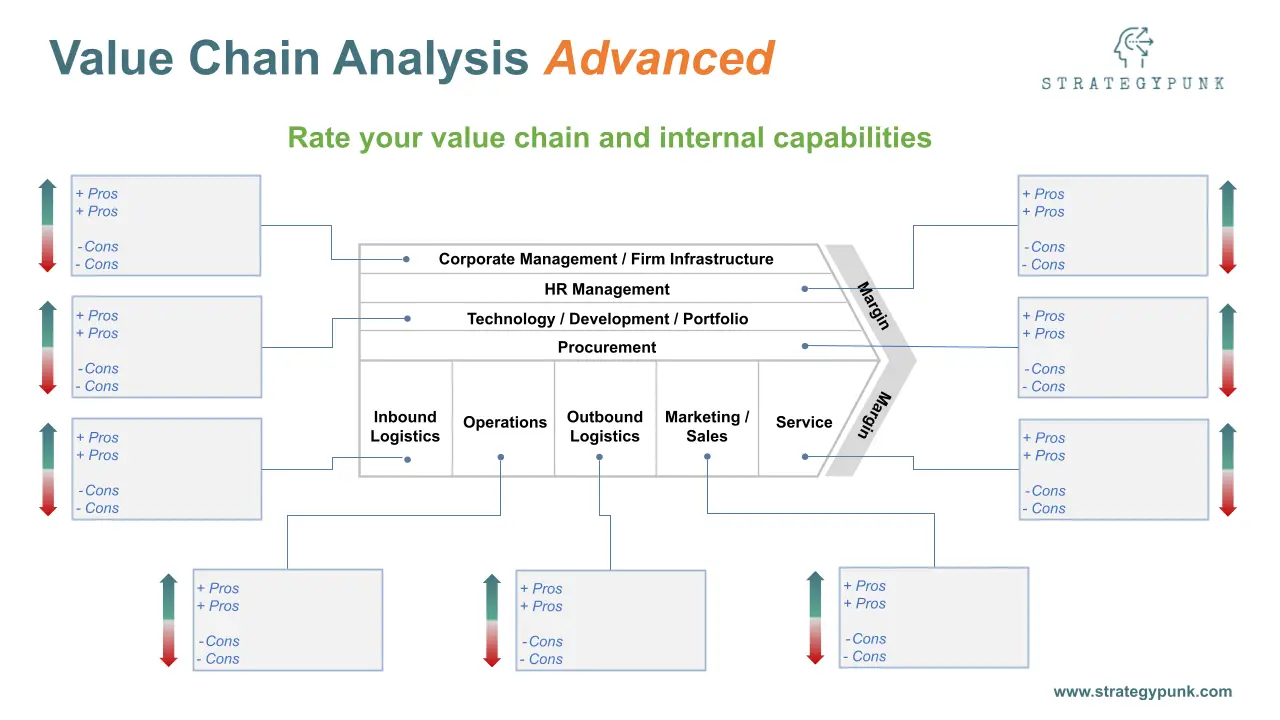
Making Sense of Porter's Value Chain
Every business is a chain of activities. Michael Porter figured this out in the 1980s, and his insight still guides companies today. Each link in the chain adds value - from getting raw materials to helping customers after a sale.
Porter's Value Chain reveals these activities. It reveals where we create value and where we lose money. Download the free PPT template below.
Why Businesses Need This
Companies face pressure. They need to cut costs, stand out, and beat competitors. The value chain gives them a map. It shows the path from suppliers to customers, points out problems, and suggests solutions.
The Building Blocks
Think of the value chain as a house. The foundation supports everything above it, and the rooms serve different purposes. Each part matters.
Primary Activities form the core:
- Inbound Logistics: You receive supplies. You store them. You track them.
- Operations: You transform materials. You build products. You create services.
- Outbound Logistics: You ship products. You deliver to stores. You reach customers.
- Marketing and Sales: You build awareness. You set prices. You close deals.
- Service: You train customers. You fix problems. You handle returns.
Support Activities hold it together:
- Infrastructure: You make plans. You manage money. You ensure compliance.
- HR: You find talent. You train people. You build teams.
- Technology: You upgrade systems. You automate tasks. You protect data.
- Procurement: You choose suppliers. You negotiate prices. You maintain quality.
Real Success Stories
Cost Leaders Win:
A factory studied its chain. It found waste in storage. It cut inventory by half. It saved millions. The prices dropped. Sales grew.
Differentiation Works:
Netflix changed entertainment. It saw gaps in the chain, cut delivery costs, made streaming easy, and created shows people wanted.
Sustainability Pays:
Patagonia looked at its chain. It found waste. It switched materials. It fixed transport. It tells customers the truth. People trust the brand.
Amazon Masters the Chain
Amazon shows the power of this thinking:
- It builds warehouses near cities
- Robots work non-stop
- Trucks run set routes
- The site knows your needs
- Help comes fast
- Problems get fixed
Put It to Work
Start small:
- Map your activities
- Track your costs
- Time your processes
- Ask your team
- Watch competitors
- Test improvements
- Measure results
Face the Challenges
The value chain has limits:
- Data hides in systems
- Teams resist change
- Markets shift fast
- Competition copies success
- Tools can conflict
The Future of Value Chains
The world changes. The chain adapts:
- Digital transforms tasks
- AI speeds decisions
- Robots join teams
- Data drives choices
- Customers expect more
Bottom Line
Porter gave us a tool. The tool still works. It shows the path to profit, points out problems, and suggests fixes. Companies that use it win, while companies that ignore it fall behind.
The value chain matters more now than ever. Markets move fast. Competition grows. Customers demand value. The chain helps you deliver it.