Plan Do Act Check (PDCA) Cycle: Free Template
Plan Do Act Check (PDCA) Cycle Framework. Guide and free PDF, PowerPoint, and Google Slides templates.
Also known as the Shewhart Cycle, Deming Cycle, or Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) Cycle
Introduction of the Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) cycle
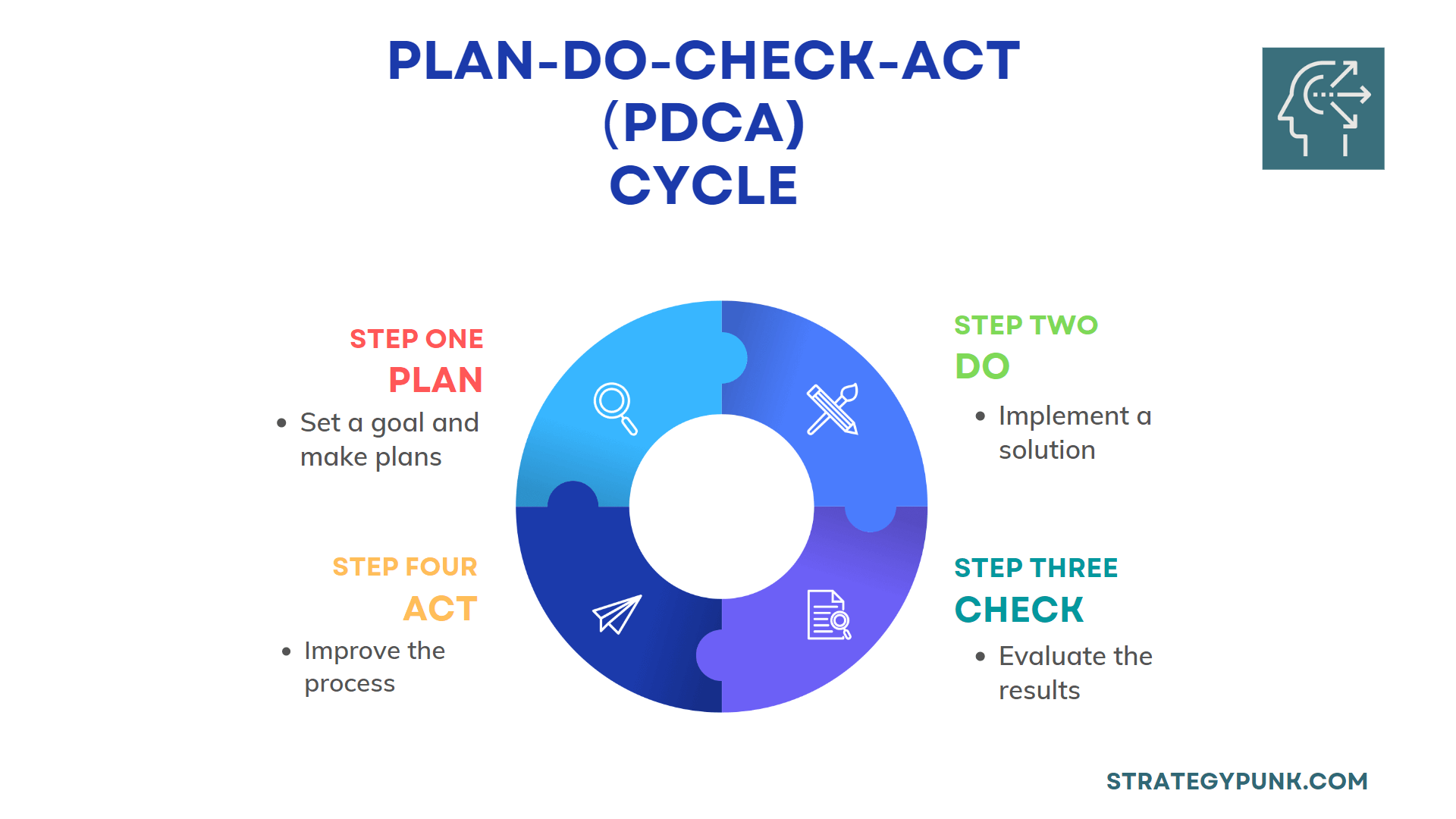
The Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) cycle is a continuous improvement methodology that is used to plan, implement, and measure the effectiveness of a process or system.
It is also known as the Deming Cycle or the Shewhart Cycle. The PDCA cycle is a four-step process that includes:
- Plan: Identify the problem or opportunity and define the goals and objectives. Develop a plan to address the issue and establish a method to measure the results.
- Do: Implement the plan and gather data on the process or system.
- Check: Analyze the data to determine if the plan was effective and if any changes need to be made.
- Act: Make necessary adjustments to the process or system and implement changes.
The PDCA cycle is an iterative process that is repeated continuously to improve the process or system.
The process is designed to be flexible, allowing adjustments and improvements to be made as needed. It is instrumental in quality management, process improvement, and problem-solving. It's widely used in many industries as a process improvement method and part of the Six Sigma methodology.
What is the PDCA Cycle?
The PDCA cycle is an iterative four-step management method for the control and continuous improvement of processes and products1.
It is also known as the Deming cycle or Deming wheel. It was named after W. Edwards Deming, who introduced PDCA in Japan in the 1950s.
The four steps of the PDCA cycle are:
Plan
Identify opportunities and plan for change.
Set goals, define the problem, analyze the current process, develop hypotheses about causes, and design a change plan.
Do
Implement the plan on a small or experimental scale.
Document problems and unexpected events, collect data, and begin analysis.
Check
Evaluate the results and compare them against the expected outcomes.
Study the actual versus expected results to determine what was learned. Identify root causes of differences.
Act
Take action to standardize the process or begin the cycle again.
Implement the solution on a broader scale or adjust the plan. Please document findings for future reference and planning.
What are the four main phases of a PDCA model?
The PDCA cycle is based on four stages: plan, do, check, and act.
The first step of the PDCA cycle is to plan, which involves identifying an initiative and defining the desired results. The second step is to do, which consists of implementing the plan. The third step is to check, which involves evaluating progress towards the goal. Finally, the fourth step is to act, which consists of taking necessary action to improve further.
Applications of the PDCA Cycle
The PDCA cycle can be applied in many areas to drive continuous improvement4:
- New process or product design and development
- Improving an existing process or product
- Problem-solving for issues in a current process
- Planning data gathering and analysis to identify problems
- Implementing any change initiative
It provides a structured approach for iterative testing and improvement.
Who created the concept of Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)?
W. Edwards Deming created the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle.
W. Edwards Deming was an American statistician, professor, author, and consultant known for his work in quality management and for introducing statistical process control, quality control, and continuous improvement methods to Japan after World War II.
He created the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle as a simple and effective tool for continuous improvement. It is widely used in various industries as a process management method. The PDCA cycle involves four steps: plan, do, check, and act, representing a systematic and continuous improvement process.
Benefits of Using the PDCA Cycle
Key benefits of the PDCA cycle include:
- Promotes continuous improvement and learning
- Minimizes risk by testing changes on a small scale first
- Engages employees in problem-solving and critical thinking
- Bases decisions on data analysis rather than assumptions
- Provides flexibility to adjust plans based on findings
- Drives standardization of successful processes
- Identifies root causes of problems or defects
Examples of PDCA Cycle Use
Many organizations across industries have used PDCA successfully6:
- Toyota continuously uses PDCA to improve its production system.
- General Electric applied PDCA to Six Sigma initiatives.
- Caterpillar used PDCA to reduce defects in its manufacturing processes.
- Florida Power & Light utilized PDCA to improve outage response time.
The PDCA cycle is a simple yet powerful tool for controlled, iterative problem-solving and process improvement.
It provides a structured approach for testing changes through planning, implementation, analysis, and action cycles.
How do you apply the Plan-Do-Check-Act PDCA cycle in a business setting?
The PDCA cycle consists of four steps: plan, do, check, and act. Each step builds on the previous one, so going through each phase is essential.
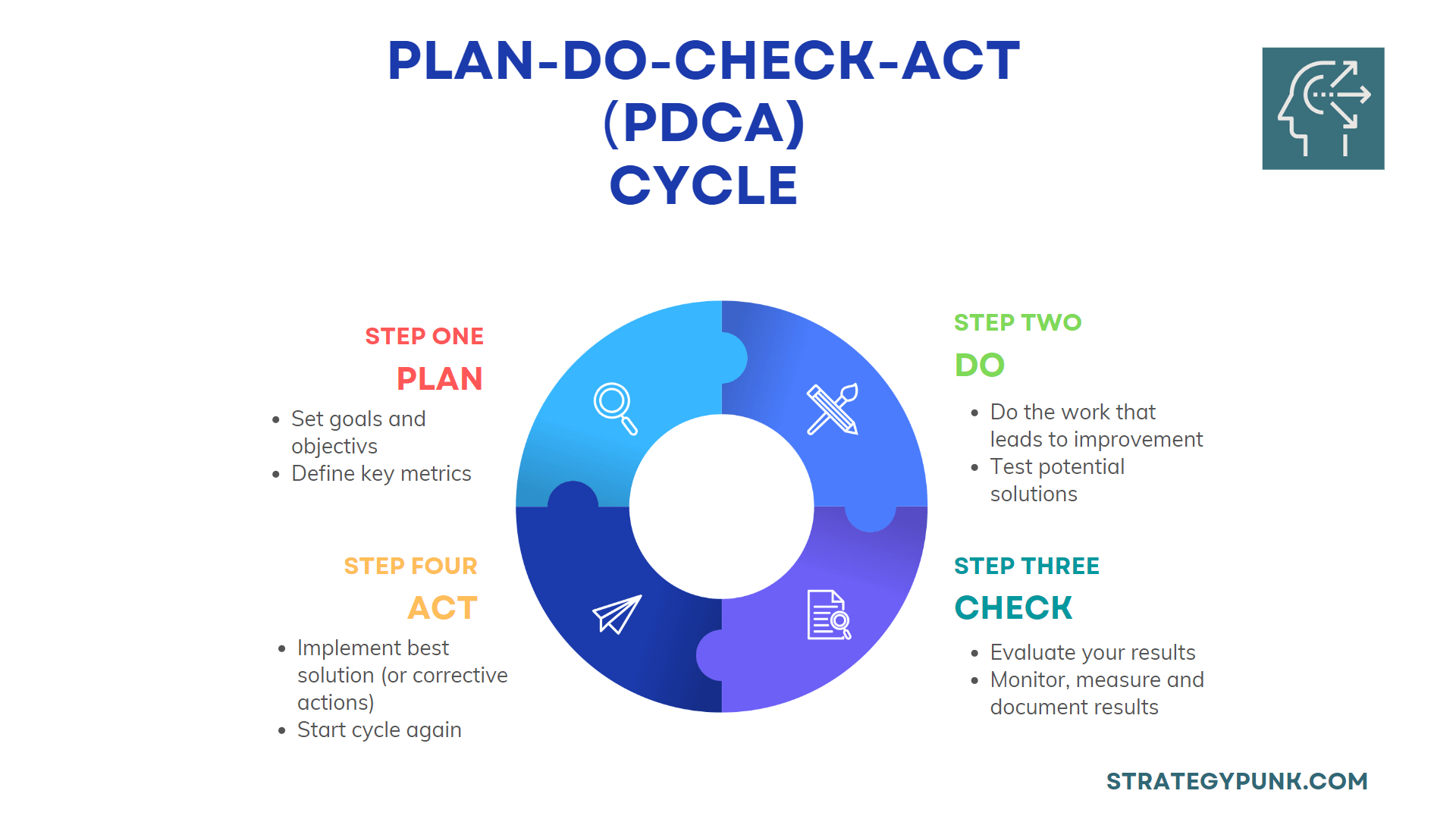
Plan
The planning step involves setting goals and objectives. This is where you define what you want to change or improve and what metrics you will use to measure your progress.
Do
The do step involves doing the work that leads to improvement. This may include changing behaviors or taking action against your metrics.
Check
The check step involves evaluating your results after you've completed the plan and done steps. This allows you to adjust your plan as necessary and as you go along.
Act
The act step involves taking action as soon as possible so that you can start seeing results sooner rather than later.
How do we measure the success of PDCA implementation?
There are several ways to measure the effectiveness and success of PDCA implementation:
Define goals and metrics
- Set specific, measurable goals for what you want to achieve through the PDCA cycle, such as reducing defects by 30% or improving customer satisfaction scores.
- Define quantifiable metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with these goals, such as the number of defects, customer satisfaction survey results, cost savings, etc. This provides concrete criteria for evaluating success.
Collect and analyze data.
- Gather relevant performance data before, during, and after the PDCA cycle. This includes process metrics, outcome metrics, and balancing measures.
- Analyze the data to identify trends and measure impact. Statistical analysis and data visualization can be helpful here.
- Compare data to baseline, goals, and past performance. Metrics should show measurable improvement.
Conduct audits and assessments
- Perform regular process audits and self-assessments to ensure compliance with new procedures and standards.
- Assess performance through observation, interviews, surveys, etc. Solicit feedback from staff and stakeholders.
- Review results to identify gaps, issues, and risks to be addressed in the next PDCA cycle.
Monitor implementation
- Track the progress of PDCA activities using tools like Gantt charts, checklists, and dashboards.
- Ensure critical steps are completed according to schedule and budget. Address delays or roadblocks promptly.
- Document lessons learned, best practices, and opportunities for improvement for the next cycle.
Link PDCA to business results
- Correlate PDCA outcomes to crucial business metrics like profits, costs, revenue, customer retention, etc.
- Show the business impact of improvements achieved through PDCA to demonstrate value and ROI.
- Use results to guide strategy and planning for future PDCA initiatives.
Measuring PDCA success requires upfront goal definition, rigorous implementation monitoring, data gathering from multiple sources, and linking outcomes to business performance.
This provides objective evidence to determine whether the PDCA cycle delivers real, sustainable improvements.
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Template
free templates in PowerPoint, PDF or Google Slides
A free and fully editable download of the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) framework in PowerPoint, PDF, or Google Slides format.
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Google Slides template
PDCA cycle in Google Slides format