Unlocking Insights: Unilever SWOT + Free PPT & PDF
Get insights from Unilever's Capital Markets Day 2024—download your free SWOT Analysis PDF and PPT templates now!
Insights derived from Capital Markets Day Presentation 2024
An Introduction to Unilever: Strategy and Business Model
Unilever is a multinational consumer goods giant operating in over 190 countries with a portfolio of more than 400 brands.
The company is a major player in personal care, home care, beauty and well-being, and food. Its products touch the lives of billions of consumers daily. In recent years, Unilever's strategy and business model have undergone significant transformations to adapt to a rapidly changing consumer landscape, intensify competition, and address past underperformance.
Growth Action Plan 2030: A Roadmap for Transformation
Unilever's current strategy is centered around its "Growth Action Plan 2030," which aims to deliver best-in-class performance through market-making, unmissably superior brands. This strategy is built on three core pillars:
- Focus: Concentrating efforts and investments on its 30 most influential brands, which account for the most turnover and profit, and prioritizing 24 key markets representing 85% of turnover.
- Excel: Driving competitive advantage and market leadership through five key areas of demand creation:
- Unmissable Brand Superiority: Achieving holistic brand excellence across all aspects, from product proposition to packaging, to command premium pricing and consumer preference.
- Multi-Year Scalable Innovations: Focusing on fewer, bigger, and better innovations that leverage science and technology to deliver sustained growth and meet evolving consumer needs.
- Social First Demand Generation: Adopting a digitally-driven marketing approach centered on social media and online channels to engage consumers, build brand loyalty, and drive demand in a rapidly changing media landscape.
- Premiumisation: Strategically shifting the portfolio towards higher-margin premium products and brands through innovation, acquisitions, and divestments.
- Growth Channels: Strengthening execution and presence in high-growth channels like e-commerce, digital commerce, and specialized retail, adapting to evolving consumer shopping behaviors.
- Accelerate: Enhancing critical capabilities in three key areas:
- Science & Technology: Investing in R&D, forging strategic partnerships, and leveraging emerging technologies like AI, biotechnology, and microbiome science to drive product innovation and accelerate time to market.
- Lean Agile Supply Chain: Optimising and streamlining the global supply chain to improve efficiency, agility, and cost-effectiveness, enabling the company to respond rapidly to changing market conditions and consumer demand.
- Scaled AI: Integrating artificial intelligence across the value chain, from demand forecasting and marketing to supply chain management and autonomous operations, to unlock efficiencies, enhance decision-making, and drive growth.
A Business Model Anchored in Strong Brands and Global Reach
Unilever's business model can be characterized as a brand-led, consumer goods powerhouse with a global reach. The company leverages its vast portfolio of iconic brands, extensive distribution network, and deep understanding of consumer needs to create and market products that meet diverse preferences across various geographies.
Key Elements of Unilever's Business Model:
- Brand Building and Marketing: Unilever invests heavily in building strong brands through marketing, advertising, and innovation. It aims to create "unmissably superior brands" that resonate with consumers and command premium pricing.
- Product Innovation and Development: Unilever focuses on continuous product innovation and development, leveraging R&D, science and technology, and consumer insights to create products that meet evolving needs and preferences.
- Global Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Unilever operates a global manufacturing and supply chain network, with factories, warehouses, and distribution centers strategically located worldwide to ensure efficient production and delivery of its products to consumers.
- Sales and Distribution: Unilever sells its products through various channels, including traditional retail, modern trade, e-commerce, and direct-to-consumer platforms, adapting to changing shopping behaviors and expanding its reach.
Evolving to Meet Future Challenges
Unilever is actively transforming its business model to address challenges like intensifying competition, changing consumer preferences, and the need for greater agility and efficiency. This involves streamlining operations, simplifying its portfolio, investing in digital transformation, and embedding sustainability into its core business practices.
Unilever's future success will depend on its ability to execute its Growth Action Plan 2030 effectively, leverage technology and innovation, adapt to evolving consumer trends, and build resilience in the face of global economic and geopolitical uncertainties.
Unilever SWOT Analysis
Strengths
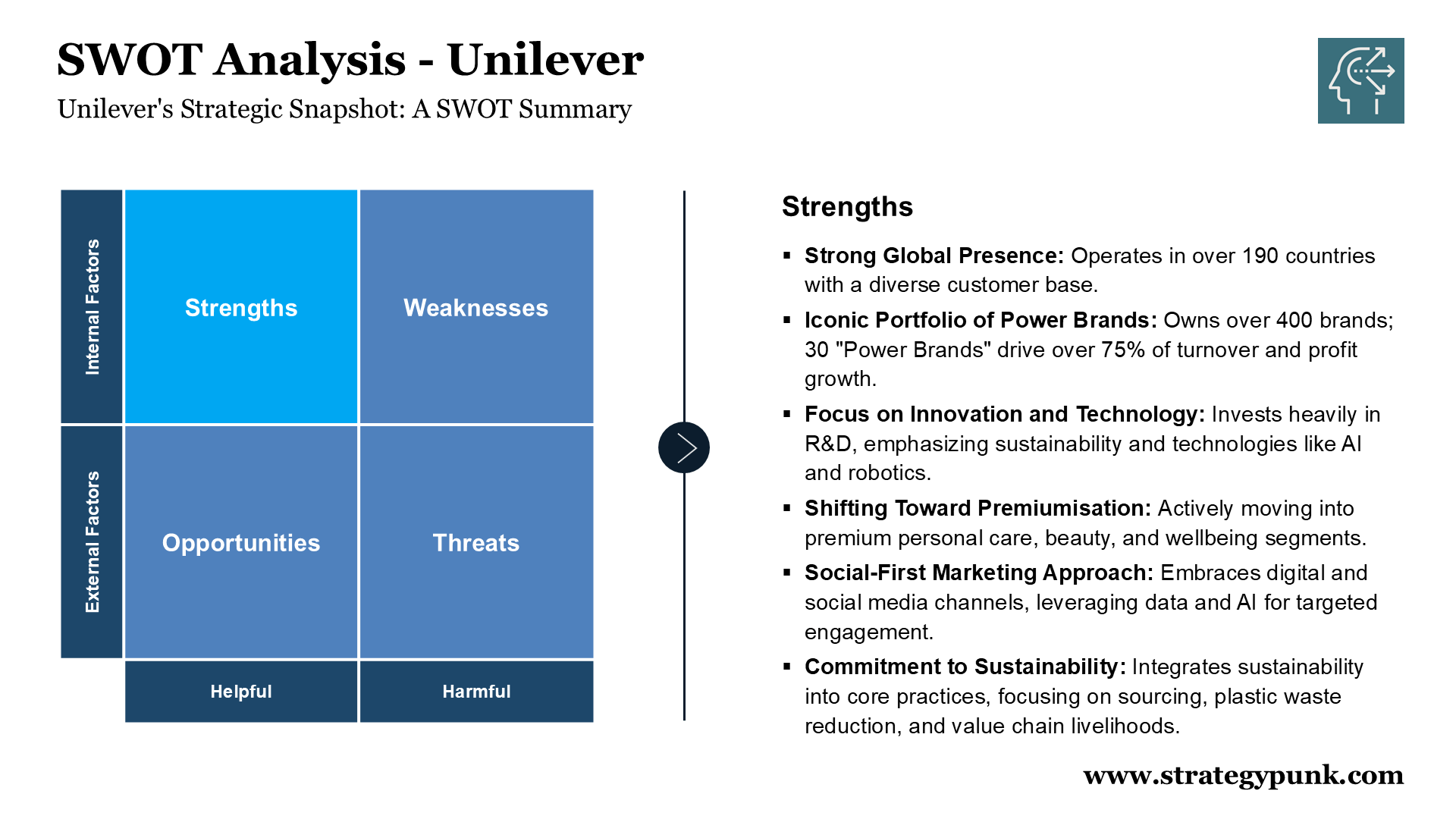
- Strong Global Presence: Unilever operates in over 190 countries, giving it a broad reach and a diverse customer base.
- Iconic Portfolio of Power Brands: Unilever owns over 400 brands, with 30 “Power Brands” accounting for over 75% of turnover and driving most profit growth. These well-established brands enjoy high consumer recognition and loyalty.
- Focus on Innovation and Technology: Unilever is committed to innovation, investing heavily in research and development (R&D), focusing on sustainability and technology like AI and robotics. This is evident in its recent Wonder Wash and Dove Serum Body Washes launches and its €100 million investment in a new fragrance creation house.
- Shifting Toward Premiumisation: Recognising evolving consumer preferences, Unilever is actively shifting its portfolio towards more premium segments within personal care, beauty, and wellbeing. This strategic move aims to capture growth in higher-margin segments and enhance brand perception.
- Social-First Marketing Approach: By embracing a social-first marketing strategy, Unilever adapts to the changing media landscape. This strategy focuses on digital and social media channels to connect with consumers. This approach leverages data and AI to create targeted and engaging content, drive demand, and build brand loyalty.
- Commitment to Sustainability: Unilever has long been a leader in sustainability, integrating it into its core business practices and brand purpose. The sources repeatedly emphasize Unilever's commitment to sustainable sourcing, reducing plastic waste, and enhancing livelihoods in its value chain.
Weaknesses
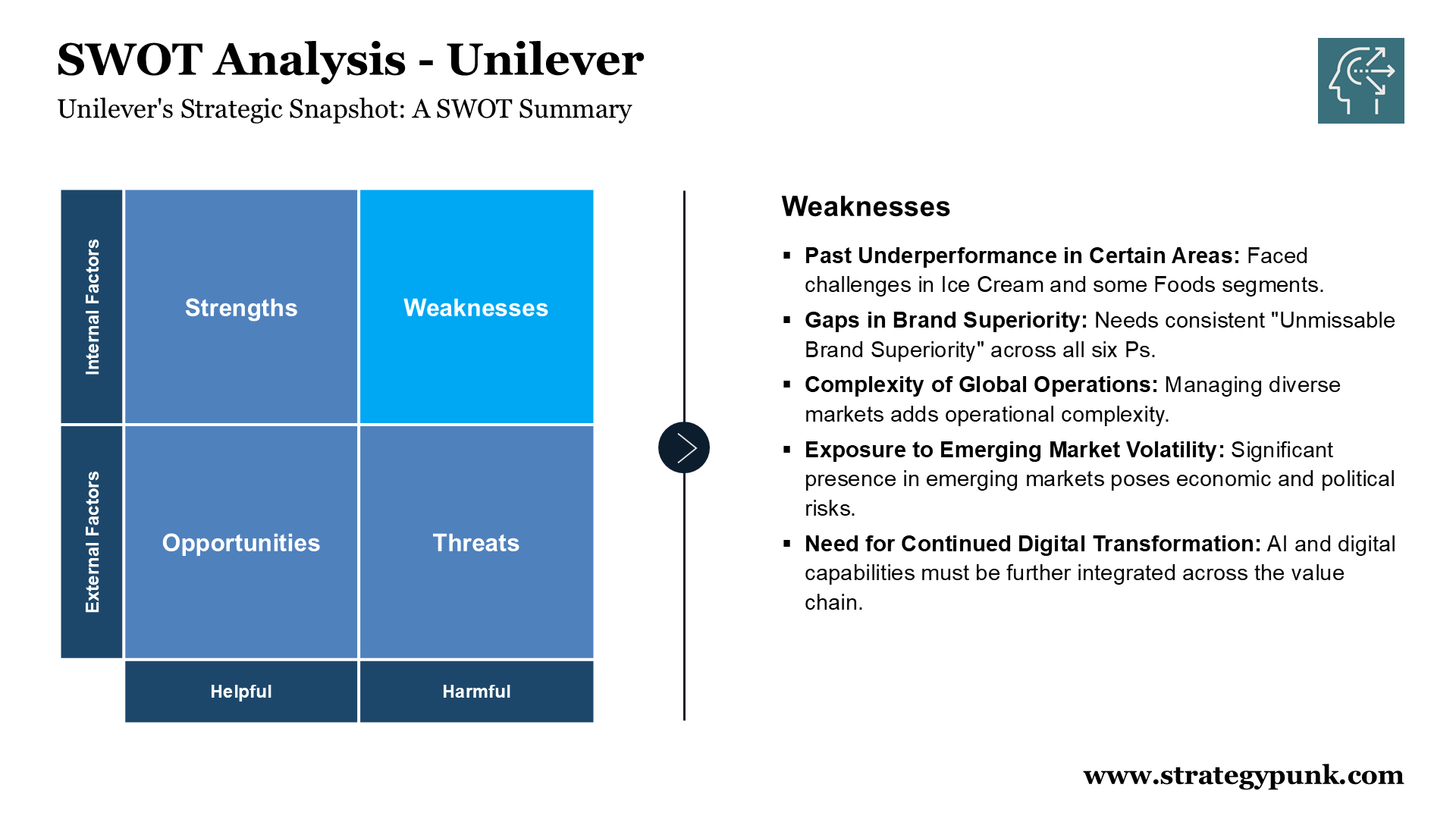
- Past Underperformance in Certain Areas: The sources acknowledge previous underperformance in some areas of the business, including Ice Cream and some areas of Foods. This highlights challenges in adapting to changing consumer preferences and maintaining market share.
- Gaps in Unmissable Brand Superiority: While many Unilever brands are perceived as superior, there are still gaps in achieving “Unmissable Brand Superiority” across all six Ps (proposition, packaging, product, promotion, place, pricing). This indicates a need to enhance brand attributes and consumer perception consistently.
- Complexity of Global Operations: Operating in numerous markets creates complexity in managing diverse consumer preferences, regulatory environments, and supply chains. The sources describe efforts to simplify and streamline operations, suggesting that complexity may have hindered efficiency and agility in the past.
- Exposure to Emerging Market Volatility: While Unilever's growth potential is strong, its significant presence in emerging markets exposes it to economic and political volatility, currency fluctuations, and commodity price fluctuations, which can impact profitability.
- Need for Continued Digital Transformation: Despite significant investments in AI and digital technologies, Unilever still needs to fully integrate these capabilities across its value chain, particularly in supply chain management and e-commerce.
Opportunities
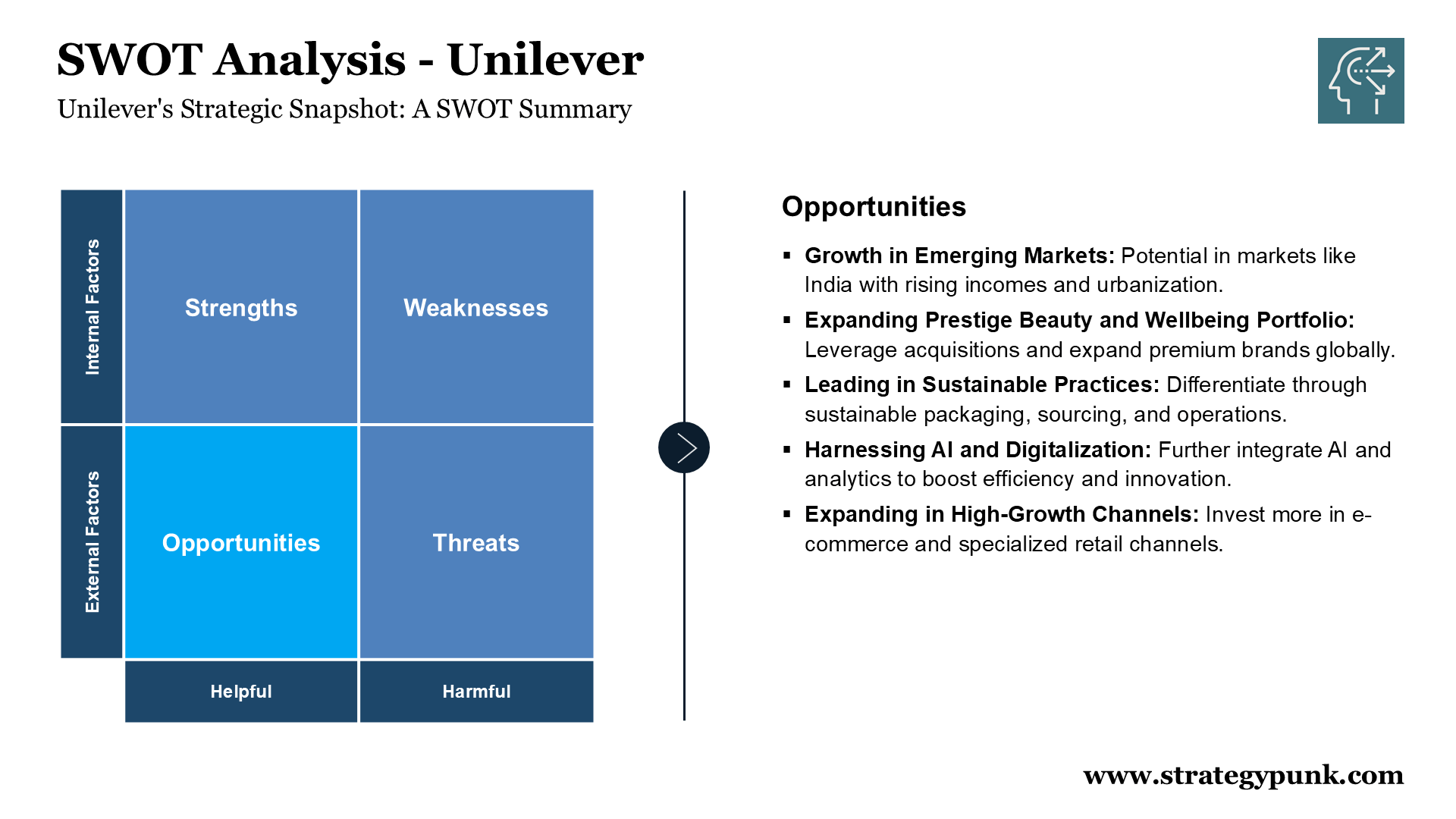
- Capitalising on Growth in Emerging Markets: The sources highlight significant growth potential in emerging markets like India, where rising incomes and urbanization drive demand for consumer goods.
- Expanding Prestige Beauty and Wellbeing Portfolio: These categories offer higher margins and growth potential. Unilever can leverage acquisitions like K18 and Hourglass and expand the global reach of premium brands like Dermalogica and Liquid I.V.
- Leading in Sustainable Business Practices: As consumer awareness of sustainability grows, Unilever can further differentiate itself by leading in sustainable packaging, sourcing, and operations.
- Harnessing the Power of AI and Digitalisation: Further integrating AI and data analytics across the value chain, from R&D to marketing and supply chain management, can unlock efficiencies, enhance consumer engagement, and drive innovation.
- Expanding in High-Growth Channels: Unilever can further invest in e-commerce, digital commerce channels, and specialized retail channels like health and beauty stores to capture growth in these rapidly expanding areas.
Threats
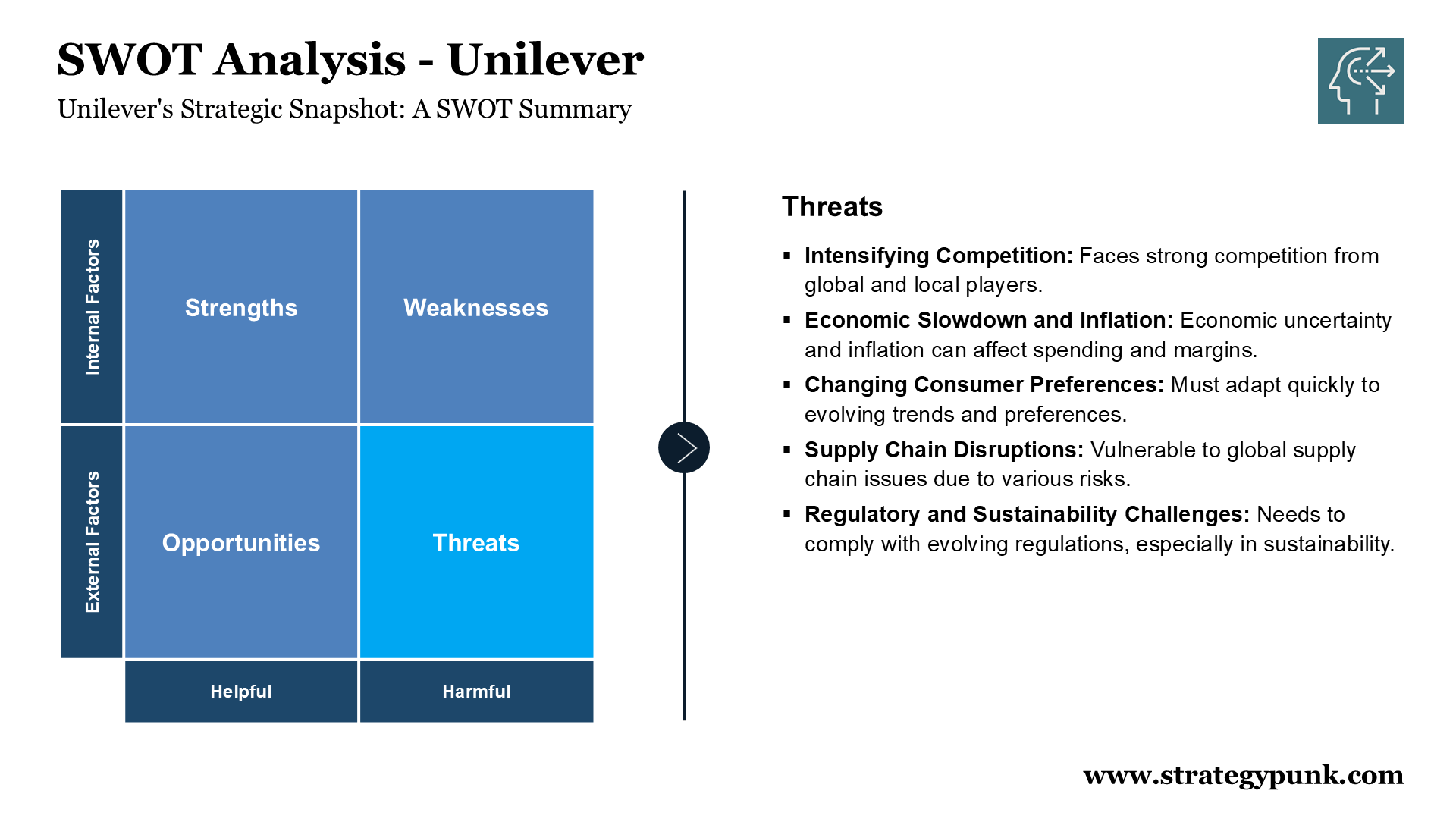
- Intensifying Competition from Local and Global Players: The consumer goods market is highly competitive, with established multinational companies and local players vying for market share. Unilever needs to innovate and differentiate itself constantly to maintain its leadership position.
- Economic Slowdown and Inflationary Pressures: Global economic uncertainty and rising inflation can impact consumer spending and pressure margins, requiring Unilever to manage costs effectively and potentially adjust pricing strategies.
- Changing Consumer Preferences and Trends: Rapidly evolving consumer preferences, particularly among younger generations, require Unilever to stay ahead of trends and adapt its portfolio and marketing strategies accordingly.
- Supply Chain Disruptions and Volatility: Global supply chains remain vulnerable to disruptions from geopolitical events, climate change impacts, and other unforeseen events. To mitigate risks, Unilever needs to build resilience and flexibility in its supply chain.
- Regulatory and Sustainability Challenges: Evolving regulations, especially those related to sustainability and packaging, require Unilever to adapt its practices and ensure compliance, which can involve additional costs and operational adjustments.
This SWOT analysis provides insights into Unilever's current position and prospects, highlighting its strengths and opportunities for growth while acknowledging areas where it needs to address weaknesses and mitigate threats.
Disclaimer: This analysis is based on Unilever Capital Markets Day 2024 and may not encompass every nuance of the company's complex strategy.