Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) Through the Lens of Venture Capital
Exploring Mergers & Acquisitions through the lens of Venture Capital: Dive into the unique insights and strategies VCs bring to the M&A landscape.

Introduction
Venture Capitalists (VCs) have a unique approach to evaluating and investing in startups, which can offer valuable insights into the Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) landscape.
While VCs focus on early-stage companies with high growth potential, M&A typically involves established companies.
However, the principles that guide VCs can be applied to M&A to enhance decision-making and outcomes.
Venture Capitalists: The Architects of Tomorrow's Giants
Venture Capitalists (VCs) shape our world. Think Google. Think Microsoft. Think life-altering COVID-19 vaccines.
Behind these game-changers? VCs.
But what's their secret sauce in picking winners? Let's unravel the VC decision-making tapestry.
VCs: More Than Just Money
VCs touch our lives daily. They bet on high-stakes startups.
The goal? Industry revolutions.
Those tech tools we can't live without? Many owe their first financial leg-up to VCs.
The VC Landscape: A Closer Look
According to a Harvard Business Review article, venture capital has been a crucial financing source for high-growth startups for over 30 years.
Companies like Amazon, Apple, and Facebook owe their early success to the capital and coaching provided by VCs. Despite their significant role, VCs' inner workings remain largely enigmatic.
VCs are pivotal in connecting entrepreneurs with good ideas to investors with capital. However, the process is more complex than it seems. Establishing value and investability for mature companies is relatively easy, given their sales, profits, and cash flow. However, for early-stage ventures, VCs must delve deeper into the business and its potential.
Mastering the Art of the Deal
Deal selection is the VC battleground. Here, startups get noticed, but it's a long road to investment.
The tool of choice? The 'deal funnel'. The stats are stark. One hundred startups enter, but only one gets the nod. It's a gauntlet. Business models get scrutinized.
Founding teams face the heat. Due diligence? Thorough.
People First, Ideas Next
VCs bet on the 'jockey,' not just the 'horse.' Could you break it down?
The 'jockey ' is the startup's human core. The 'horse' is the product, tech, and model. The bottom line is trust. VCs need to believe in the team.
A brilliant idea without stellar leadership? It's a non-starter.
VCs: A Breed Apart
They're not your regular investors. VCs play a different game. They cast a wider net. Embrace bigger risks. And they don't go it alone. Co-investing is common.
Traditional financial yardsticks? Often sidelined. Predicting a startup's cash flow is a guessing game, especially when data is a mirage.
An Investopedia article explains what prompts VCs to invest. Key considerations include solid management, market size, product quality, and risk assessment.
VCs prioritize experienced management teams. They also seek large, addressable markets, ideally worth over $1 billion. The product or service should have a competitive edge, and the risks associated with the investment should be clear.
Life Lessons from VCs
Not a startup enthusiast? No matter. The VC way has lessons for all. Embrace risks. Stay nimble. Keep an open mind. Rewards await. It's about research. But also about daring to try. Success in business mirrors success in life.
To wrap up, VCs are trailblazers. Their investment approach? Enlightening. Their impact? Monumental. Dive into the VC mindset. It's a masterclass in innovation and success.
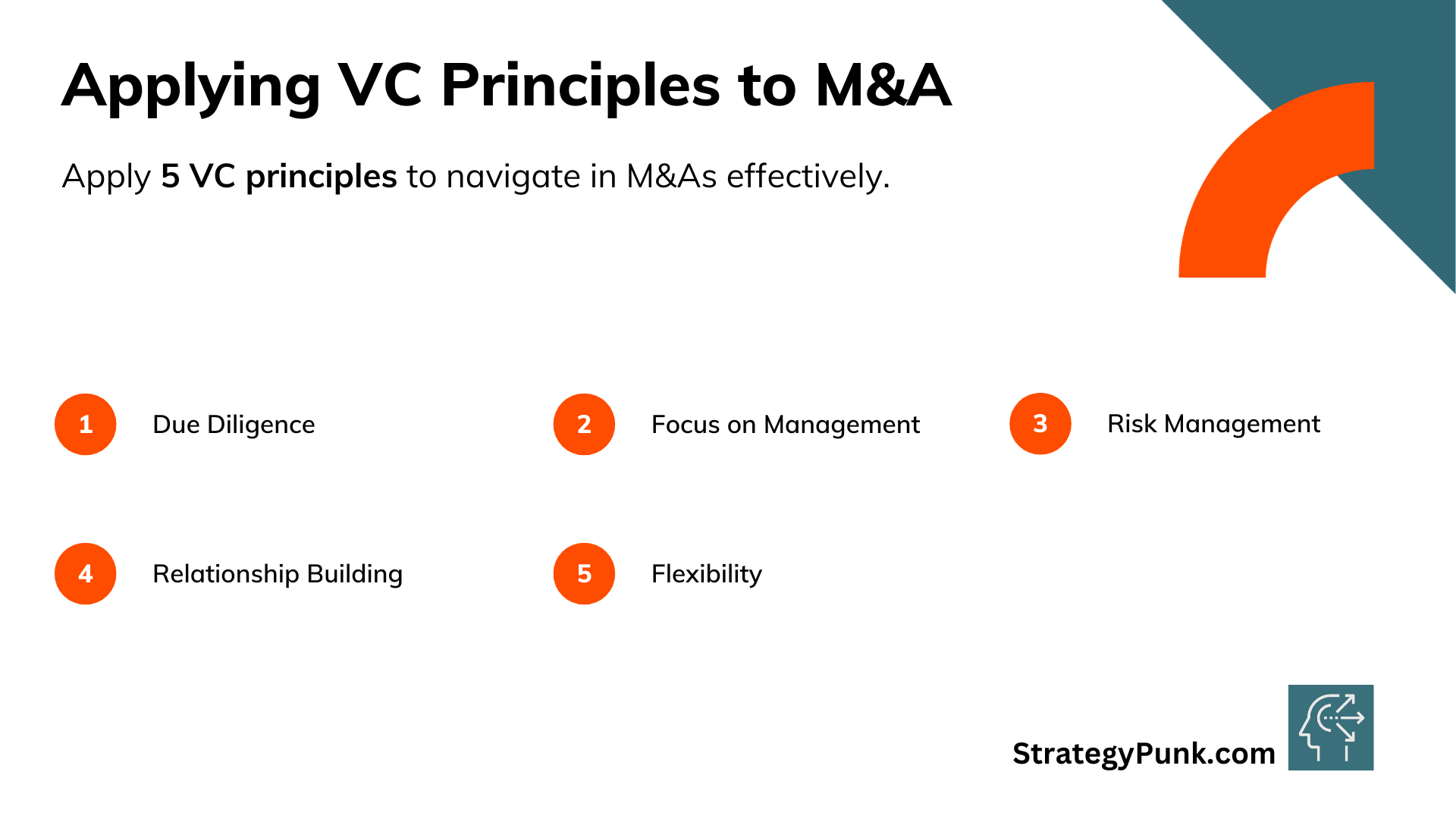
Applying 5 VC Principles to M&A
Due Diligence
Just as VCs conduct thorough due diligence before investing in a startup, M&A professionals should also conduct comprehensive research and analysis of potential acquisition targets.
Focus on Management
VCs prioritize the management team when evaluating startups. Similarly, in M&A, the leadership and management of the target company play a crucial role in the acquisition's success.
Risk Management
VCs are known for their high-risk, high-reward approach. In M&A, understanding and managing risks associated with the acquisition can lead to better outcomes.
Relationship Building
VCs often co-invest with other firms, building a network of relationships. In M&A, fostering connections with other companies, investment banks, and advisors can open up more opportunities and provide valuable insights.
Flexibility
VCs maintain an open mind and are willing to pivot when necessary. M&A professionals should also be adaptable and ready to adjust their strategies based on market conditions and new information.
In conclusion, while Venture Capital and Mergers & Acquisitions operate in different spheres, VC decision-making principles can offer valuable insights for M&A professionals.
By understanding and applying these principles, M&A professionals can enhance their decision-making processes, leading to more successful acquisitions and mergers.
Executive Summary

Executive Summary: Mergers & Acquisitions Through the Lens of Venture Capital
- Venture Capitalists (VCs):
- Drive growth in startups with high potential.
- Have unique evaluation criteria, offering insights for M&A.
- VC Impact:
- Behind tech giants like Google and Microsoft.
- Play a pivotal role in shaping industries.
- VC Decision-making:
- 'Deal selection' is crucial.
- Only one in a hundred startups typically gets funded.
- People vs. Product:
- VCs prioritize the startup's team over the product.
- Trust in the team's ability to execute is paramount.
- VCs vs. Traditional Investors:
- VCs take more significant risks and co-invest.
- Traditional financial models often don't apply.
- Applying VC Principles to M&A:
- Emphasize due diligence and focus on management.
- Understand risks and build relationships.
- Key Takeaway:
- VC principles offer valuable insights for M&A.
- Both aims for growth, but their approaches differ.
Frequently Asked Questions
on M&A, CVC, and VC

What is M&A for a VC?
For a Venture Capitalist (VC), Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) represent strategic opportunities.
They offer an exit path for investments, allowing VCs to realize returns. When a startup they've funded merges with or gets acquired by a larger entity, it typically signals success. The VC's stake in the startup is converted into cash or shares of the acquiring company.
M&A also showcases a VC's ability to nurture and guide startups to attractive exit points. It enhances their reputation in the investment community. Successful exits attract more investors to the VC's fund and more startups seeking guidance.
In essence, M&A is a testament to a VC's investment acumen. It's the culmination of their efforts, marking the transition of a startup from a high-risk venture to a recognized entity in the market.

What is a business's M&A strategy?
A business's M&A strategy defines its approach to mergers and acquisitions. It outlines how a company plans to grow, diversify, or consolidate its position by buying, merging, or selling other entities. This strategy aligns with the company's broader goals, whether entering new markets, acquiring new technologies, or eliminating competition.
Executing an M&A strategy requires rigorous due diligence. Companies assess potential targets or partners based on financial health, cultural fit, and strategic alignment. They evaluate risks, anticipate challenges, and determine the possible return on investment.
In essence, an M&A strategy is a roadmap. It guides businesses in making informed decisions about which entities to join forces with or acquire, ensuring that each move propels the company closer to its objectives.

What is the difference between CVC and M&A?
Corporate Venture Capital (CVC) and Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) are distinct strategic approaches businesses use to drive growth and innovation.
CVC involves corporations directly investing in external startups or emerging companies. Through CVC, companies tap into new technologies, markets, or business models. They don't acquire these startups but take minority stakes, fostering innovation without complete ownership.
M&A, on the other hand, involves one company buying or merging with another. The goal? Expand operations, reduce competition, or acquire valuable assets. In M&A, the developing company takes control, integrating the target company's operations, assets, and personnel.
While CVC seeks collaboration and shared growth with startups, M&A aims for consolidation and direct expansion.

What is the primary purpose of M&A?
The primary purpose of M&A is growth. Companies use mergers and acquisitions to expand their operations, reach, or market share. By acquiring or merging with another entity, a company can quickly tap into new markets, customer bases, or technologies.
M&A also offers cost efficiencies. Companies can eliminate redundancies, streamline operations, and achieve economies of scale. This consolidation often leads to increased profitability.
Lastly, M&A can reduce competition. Companies can dominate their market segment by merging with or acquiring competitors, setting the stage for increased pricing power and market influence.

What are the keys to successful M&A?
Successful M&A hinges on due diligence. Companies must thoroughly assess potential targets' financial, operational, and cultural aspects. Understanding liabilities, synergies, and possible roadblocks is crucial.
Integration planning is vital. Post-acquisition, aligning operations, technologies, and teams ensure a smooth transition. Clear communication, both internally and externally, mitigates uncertainties and fosters collaboration.
Lastly, cultural alignment matters. Merging distinct corporate cultures requires sensitivity and strategy. Ensuring shared values and goals paves the way for a united, productive entity.

What are the two sides of M&A?
The buy-side refers to the acquirer. This party is on the hunt to purchase or merge with another company. They scout potential targets, assess their value, and initiate acquisition. Their objective? Drive growth, access new markets, or harness innovative technologies.
The sell-side represents the target. This entity is up for sale or merger. They present their company's value, assets, and potential to prospective buyers. Their goal? Achieve a favorable deal, maximize shareholder value, and ensure a seamless integration.

What is an example of an M&A strategy?
An example of an M&A strategy is a tech company's plan to expand its product offerings through acquisitions.
Imagine TechGiant Inc., a leading software company. They dominate the desktop software market but need a solid mobile application suite. Instead of building a mobile platform from scratch, they target AppStart Co., a rising star in mobile app solutions.
TechGiant's strategy is acquiring AppStart to tap into its innovative mobile technologies. This move accelerates TechGiant's entry into the mobile space and eliminates a budding competitor. Post-acquisition, TechGiant integrates AppStart's offerings into its product line, providing a comprehensive software solution for its customers.
Through this M&A strategy, TechGiant swiftly expands its market reach, strengthens its product portfolio, and positions itself as a holistic software solution provider.
Interesting Resources
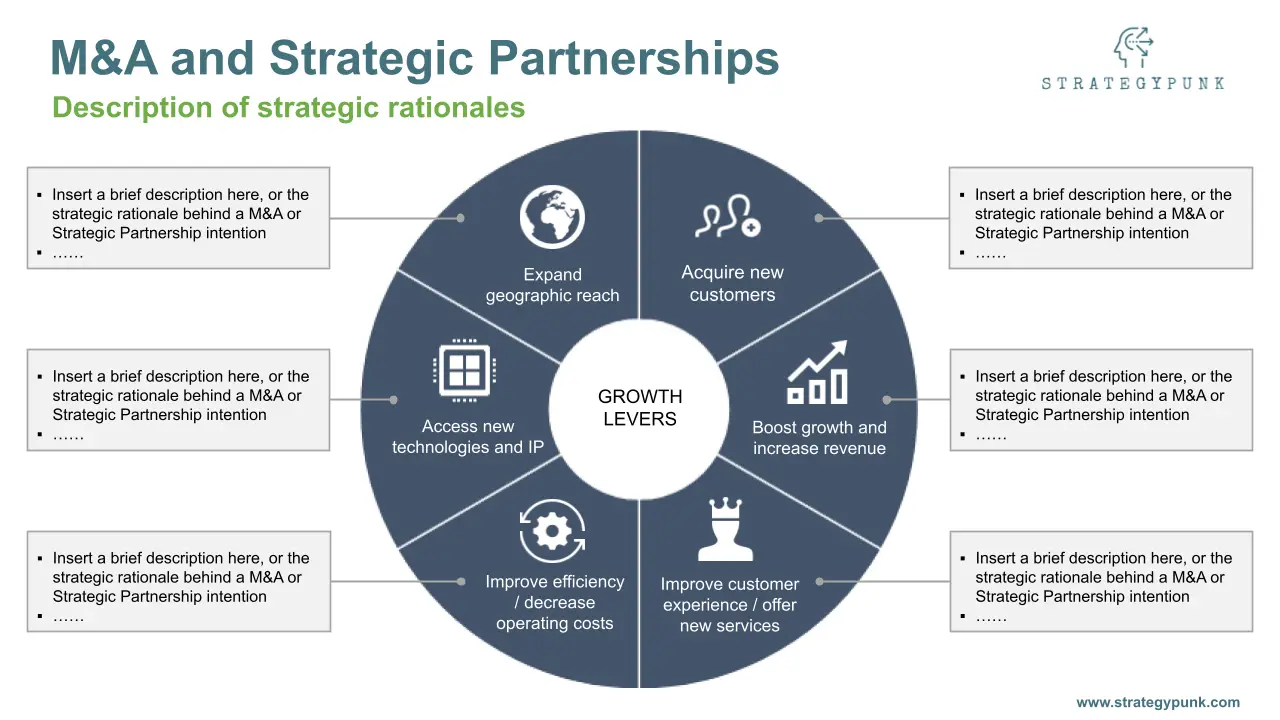
M&A and Strategic Partnerships: PowerPoint Evaluation tool
M&A and Strategic Partnerships: Free PowerPoint Evaluation tool. A simple evaluation tool to describe and rate the strategic rationales of M&A projects or strategic partnerships.
Mergers and Acquisitions Explained: A Crash Course on M&A (Free Templates)
Unlock the strategic power of Mergers and Acquisitions with our comprehensive guide. From types of transactions to key players, we break down the complexities of M&A, providing a crash course that drives growth and transformation in the business world.
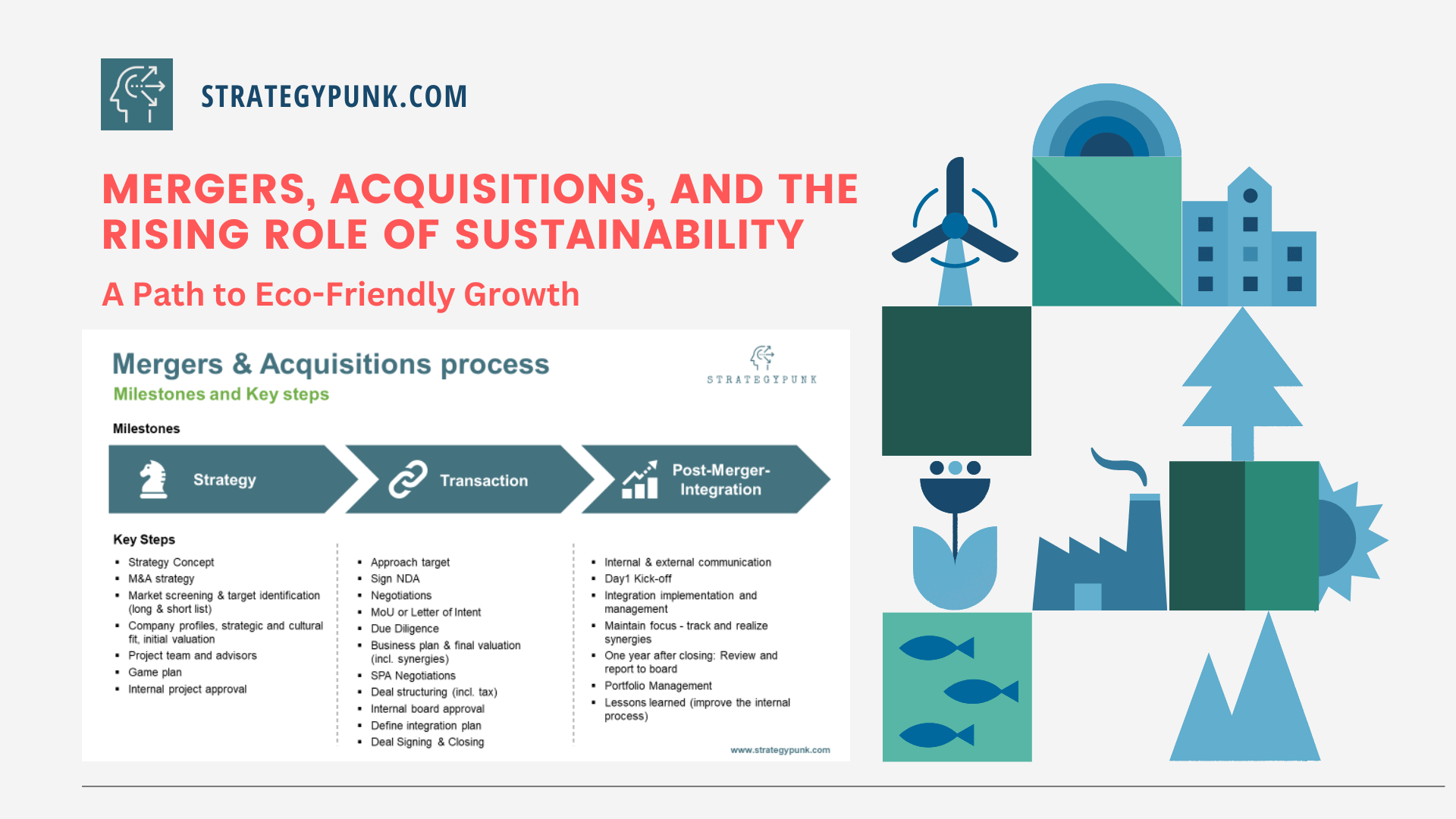
Mergers, Acquisitions, and the Rising Role of Sustainability
ESG is reshaping M&A, affecting deal valuation, investor demands, regulatory compliance, and integration strategies.