SWOT Analysis Volvo (based on Capital Markets Day 24)
Volvo's SWOT analysis shows a strong brand and tech focus but faces challenges like China dependence and competition. Download the free PDF.

Volvo Cars Strategy: A Comprehensive Overview
Volvo Cars' strategy is about growth and innovation and putting the customer at the heart of its operations. Their plan is built upon five key pillars, all designed to enhance the customer experience, making you, our valued stakeholders, integral to our operations.
1. Leading the Charge in Electrification and Sustainability:
- Volvo Cars' unwavering commitment to becoming a leader in transitioning to electric vehicles and reducing its environmental impact is a testament to its dedication to sustainability.
- Their target is 50-60% of global sales to be electrified by 2025 and 90-100% by 2030. This includes fully electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles, allowing them the flexibility to meet diverse market demands and infrastructure readiness.
- They invest in various electrification technologies, including in-house development of e-motors, a 'cell-to-body' battery technology for SPA3 vehicles, and strategic partnerships for battery cell sourcing.
- Volvo is firmly focused on reducing CO2 emissions across its operations and supply chain, with ambitious targets of a 30-35% reduction per car by 2025 and 65-75% by 2030, instilling hope about our significant environmental impact.
- The development of the EX30, their smallest SUV with the lowest carbon footprint to date, demonstrates this commitment.
2. Driving Growth in the Premium Segment:
- Volvo Cars aims to outpace the growth of the premium car market while prioritizing value creation over chasing specific revenue targets.
- They plan to achieve this by focusing on the fastest-growing segments within the premium market, particularly premium electric vehicles.
- Volvo is expanding its product line-up to cater to a broader range of customer needs and preferences, with a balance of fully electric and hybrid models.
- Key models driving growth include the new fully electric EX90, designed to redefine the premium electric SUV segment, and the EX30, which has already achieved significant success in markets like Europe and Latin America.
- In addition to new models, Volvo is also introducing upgrades to existing hybrid vehicles, ensuring they remain competitive and appealing in the transition phase.
3. Achieving and Exceeding Profitability Goals:
- Volvo Cars is targeting an EBIT margin of 7-8% by 2026.
- To achieve this, they are focusing on a multi-pronged approach:
- Growth: While not the primary lever for profitability, Volvo expects its expanded product portfolio and strategic positioning in growing segments to contribute to increased sales and revenue.
- Market Normalisation: They anticipate pricing becoming more competitive as the electric vehicle market matures. Volvo is confident in retaining its premium pricing position through its superior technology and enhanced customer experience.
- Fixed Cost Efficiencies: Volvo is implementing targeted cost actions across its business, focusing on R&D cost reductions enabled by its 'superset tech stack.'
- Technology Investments: They invest strategically in new technologies to enhance their vehicles and reduce variable costs, improving gross margins.
- The development of their SPA3 platform and the 'superset tech stack,' which enables the efficient development and production of a range of models, is central to this strategy.
- Looking beyond 2026, Volvo sees further profit opportunities as more products benefit from these technology investments.
4. Optimising the Global Footprint for Flexibility and Efficiency:
- Volvo Cars has a robust global footprint, with operations in Europe, Asia, and the United States, which provides flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions and manage geopolitical risks.
- They follow a "build where we sell" and "source where we build" strategy, allowing them to leverage regional strengths and reduce transportation costs.
- Their production of SPA1 vehicles exemplifies this strategy in all three regions, their flexible Torslanda plant in Sweden, which can build five different models, and their plans for SPA3 production across all regions.
- They are also strengthening their global footprint through strategic investments, including:
- New manufacturing facilities, like the fully electric plant in Kosice, Slovakia, which will pioneer new efficiency initiatives.
- Battery technology investments, focusing on a geographically spread and hedged strategy using a mix of partners and technologies.
- Investments in mega casting technology, first at their Torslanda plant and later in Kosice and Daqing, to lower costs, reduce complexity, and create lighter cars.
5. Expanding Beyond Cars and Prioritising the Customer Experience:
- Volvo Cars is expanding its offerings beyond traditional vehicles to create a comprehensive ecosystem for customers.
- This includes:
- Service plans, which help retain customers and generate revenue from older vehicles.
- Car insurance, providing another revenue stream and directing repairs to authorized retailers.
- Energy solutions, such as home charging systems, battery energy storage, and intelligent charging functionality, further support the transition to electric mobility and create a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
- Alongside these offerings, Volvo focuses on creating a seamless omnichannel customer experience.
- This includes a direct-to-consumer model in specific markets, strong collaboration with its global network of retail partners, and a focus on consistently high service levels in every touchpoint.
Volvo Cars believes these strategies will position them for success in the coming decade, enabling them to deliver on their purpose of providing customers with the freedom to move in a personal, sustainable, and safe way.
Volvo Cars Business Model: A Deep Dive
Volvo Cars' business model is multifaceted, evolving beyond manufacturing and selling automobiles. The sources provide insights into their approach:
1. Premium Positioning and Value-Driven Growth:
- Volvo Cars is a premium car brand emphasizing safety, sustainability, human-centric technology, and Scandinavian design.
- This allows them to command premium pricing, a key driver of profitability.
- Their focus is on value creation rather than solely pursuing sales volume, reflected in their aim to outgrow the premium car market.
- They prioritize delivering a high-quality customer experience, enhancing brand loyalty and willingness to pay.
2. Global Reach with a "Build Where We Sell" Strategy:
- Volvo Cars has a robust global footprint with operations in Europe, Asia, and the United States.
- They follow a "build where we sell" strategy, producing vehicles locally to serve key markets and manage geopolitical risks.
- This is exemplified by their production of SPA1 vehicles in all three regions and their plans to produce the upcoming SPA3 platform globally.
- They also aim to "source where we build," reducing transportation costs and supporting local economies.
3. Embracing Electrification with a Balanced Portfolio:
- Volvo Cars is at the forefront of the transition to electric vehicles, aiming to electrify 90-100% of its sales by 2030.
- They offer a balanced portfolio of fully electric, plug-in hybrid, and mild hybrid vehicles to cater to varying market demands and infrastructure readiness.
- They invest heavily in electrification technologies, including in-house development of e-motors and battery packs and strategic partnerships for battery cell sourcing.
- Their focus on long-range plug-in hybrids serves as a bridge for customers not yet ready for fully electric vehicles.
4. Technological Innovation as a Core Differentiator:
- Volvo Cars invests heavily in technology to enhance safety, customer experience, and operational efficiency.
- Their development of a "superset tech stack" is a key strategic pillar, enabling the efficient development and production of a wide range of models.
- This tech stack includes core computing, 5G connectivity, a centralized data center, and ecosystem integration, supporting features like over-the-air updates and advanced driver-assistance systems.
- They leverage AI and machine learning to analyze real-time data, continuously improving their vehicles' safety and performance.
5. Expanding Beyond Cars to Create a Comprehensive Ecosystem:
- Volvo Cars is expanding its offerings beyond traditional vehicles to create a more comprehensive ecosystem for customers.
- This includes:
- Service plans to enhance customer retention and generate recurring revenue.
- Car insurance is offered through partnerships, providing an additional revenue stream and directing repairs to authorized retailers.
- Energy solutions such as home charging, battery energy storage, and intelligent charging functionality to support the transition to electric mobility.
- These offerings aim to make car ownership more hassle-free, provide additional value to customers, and create new revenue streams for the company.
6. Strategic Partnerships to Enhance Capabilities:
- Volvo Cars actively collaborates with technology leaders to enhance its capabilities and access cutting-edge technologies.
- These partnerships include collaborations with:
- Google for Android Automotive OS and embedded Google services.
- Qualcomm for high-performance processors and connectivity solutions.
- NVIDIA for core computing platforms and AI capabilities.
- Luminar for lidar technology for advanced safety and driver-assistance systems.
- They also host events like the Automotive Technology Leaders’ Roundtable to foster collaboration and innovation within their supply chain.
7. Customer-Centric Approach and Omnichannel Experience:
- Volvo Cars is committed to a customer-first approach, aiming to provide a seamless omnichannel experience.
- They are transitioning to a direct-to-consumer model in specific markets, providing transparent pricing and simplified options.
- They also recognize the importance of their retailer network, collaborating to provide a consistently high level of service and a premium brand experience.
- Their investment in consumer data and CRM capabilities supports their efforts to personalize the customer experience.
In summary, Volvo Cars' business model is evolving to meet the demands of a rapidly changing automotive landscape.
Their strategy combines a focus on electrification, technology-driven innovation, a global footprint, and a customer-centric approach to position them for sustainable growth and profitability in the years to come.
What are Volvo Cars' five key strategic objectives for the next decade?
Here are five key strategic objectives for Volvo Cars over the next decade, based on the capital markets day:
- Lead in Electrification and Sustainability: Volvo Cars aims to lead the transition to electric vehicles and minimize environmental impact. By 2025, they aim for 50-60% of global sales to be electrified (fully electric and plug-in hybrid), increasing to 90-100% by 2030. They also have industry-leading ambitions for CO2 reduction per car, aiming for a 30-35% reduction by 2025 and 65-75% by 2030.
- Outgrow the Premium Car Market: By focusing on value creation rather than solely pursuing revenue targets, Volvo aims to outpace the growth of the premium car market. They plan to achieve this through premium pricing, competitive electric vehicle offerings, and expansion into new markets and segments.
- Achieve and Exceed Profitability Targets: Volvo aims for an EBIT margin of 7-8% by 2026. They plan to achieve this through growth, market normalization, fixed cost efficiencies, and benefits from their technology investments, which they expect to outweigh headwinds from depreciation and amortization significantly. Beyond 2026, they see further profit opportunities as more products leverage their 'superset tech stack' and SPA3 technology.
- Strengthen and Expand the Global Footprint: Volvo will continue to expand its global footprint, adapting to market changes and optimizing its end-to-end value chain. This includes building cars where it sells them, sourcing where it creates them, and strategically partnering with selected suppliers. Volvo will also continue to invest in battery technology, focusing on geographic spread and a mix of partners and technologies.
- Expand "Beyond Car" Offerings and Enhance Customer Experience: Volvo will continue expanding its offerings beyond vehicles. This includes service plans, insurance, and energy solutions (home charging, battery energy storage, and intelligent charging functionality). Volvo aims to create a seamless omnichannel customer experience, making car ownership hassle-free and providing a premium experience at every touchpoint.
These objectives represent a comprehensive approach to navigating the evolving automotive landscape, focusing on sustainable growth, technological leadership, and a customer-centric approach.
SWOT Analysis Volvo
based on Capital Markets Day 2024
Volvo Cars is an automotive company focused on safety and sustainability. This SWOT analysis examines Volvo's market position and outlines its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The insights are based on presentations from Volvo's Capital Markets Day 2024.
Understanding these factors can shed light on Volvo's future direction.
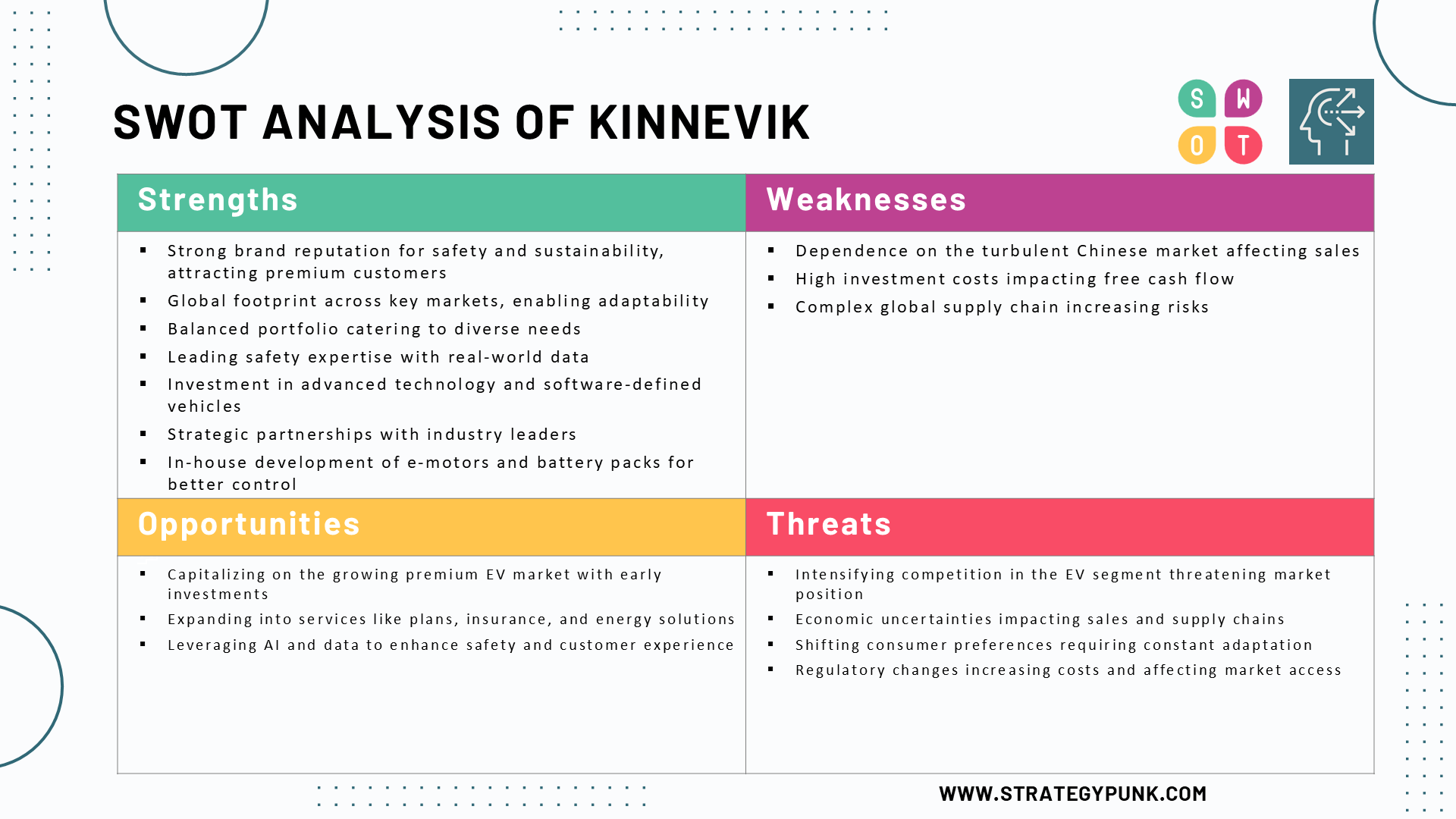
SWOT Analysis of Volvo Cars
Here is a SWOT analysis of Volvo Cars based on the presentations provided for the Capital Markets Day 2024:
Strengths:
- Strong Brand Reputation: Volvo has a strong brand reputation, particularly regarding safety and sustainability. This helps them command premium pricing and attract customers who align with these values.
- Global Footprint: Volvo has a robust global footprint with operations in Europe, Asia, and the United States. This allows them to adapt to market changes, leverage regional strengths, and manage geopolitical risks.
- Balanced Portfolio: Volvo offers a balanced portfolio of fully electric, plug-in hybrid, and mild hybrid vehicles. This flexibility caters to varying customer needs and market readiness for electrification.
- Leading Safety Expertise: Volvo is renowned for its safety innovations and has a long research and development history in this area. Their focus on real-world data and stringent safety standards sets them apart.
- Focus on Technology: Volvo invests heavily in technology, particularly its 'superset tech stack,' core computing, and software-defined vehicles. This will enhance customer experience, improve safety, and enable continuous improvement through over-the-air updates.
- Strategic Partnerships: Volvo actively collaborates with technology leaders such as Google, Qualcomm, NVIDIA, and Luminar. These partnerships give them access to cutting-edge technology and expertise.
- In-house Expertise: Volvo is developing key technologies in-house, such as e-motors and battery packs. This gives them greater control over performance, cost, and efficiency.
Weaknesses:
- Dependence on China: While Volvo has a global presence, China remains a crucial market, and the current turbulence in the Chinese market presents a challenge.
- High Investment Costs: Volvo is in a peak investment phase, impacting its free cash flow in the short term.
- Complex Global Supply Chain: Managing a global supply chain with diverse sourcing and production locations involves inherent complexities and risks.
Opportunities:
- Growing Premium EV Market: The premium electric vehicle market is experiencing strong growth, offering Volvo a significant opportunity, particularly given its early investments in this area.
- Expansion of 'Beyond Car' Offerings: Volvo expands beyond cars to include service plans, insurance, and energy solutions. This diversification can create new revenue streams and strengthen customer relationships.
- Leveraging AI and Data: Volvo can further leverage AI, machine learning, and real-time data to enhance safety, improve customer experience, and optimize operations.
Threats:
- Intensifying Competition: Competition in the automotive industry, particularly in the electric vehicle segment, is intensifying.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Geopolitical tensions, trade tariffs, and macroeconomic challenges can impact sales, profitability, and supply chains.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements require continuous adaptation to stay relevant.
- Regulatory Changes: Regulation changes, particularly regarding emissions and safety standards, can impact development costs and market access.